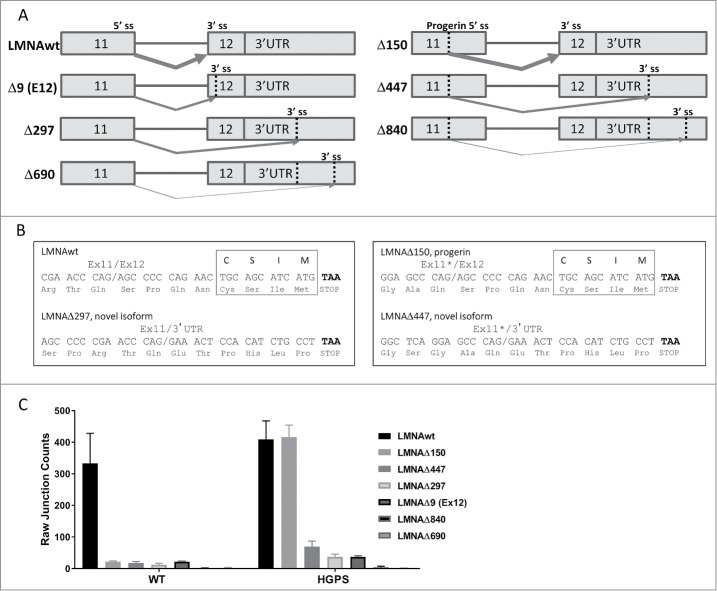
Figure 1.
Novel isoforms of LMNA detected by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). (A) Schematic representation of alternatively spliced isoforms LMNAwt, LMNAΔ150, LMNAΔ447, LMNAΔ297, LMNAΔ9(ex12), LMNAΔ840, and LMNAΔ690. Vertical dotted lines indicate alternative splice donor or acceptor sites (labeled “ss”). Arrows indicate predicted splice junction for each isoform, varying thickness indicates relative expression level. (B) Predicted C-terminus nucleotide and amino acid sequences for LMNAwt, LMNAΔ150, LMNAΔ297, and LMNAΔ447. The exon 11/exon 12 (or 3′ UTR) junction is indicated with a slash, truncated exon 11 with cryptic 5′ splice site use is marked with an asterisk, stop codon is highlighted in bold, and farnesylation motif “CSIM” is indicated for LMNAwt and LMNAΔ150 isoforms. (C) Splice junction counts by RNA-seq. Splice junction counts in wild type and HGPS fibroblasts are shown for LMNAwt, LMNAΔ150, LMNAΔ447, LMNAΔ297, LMNAΔ9(ex12), LMNAΔ840, and LMNAΔ690. Values represent averages +/− SD from 3 independent replicates.