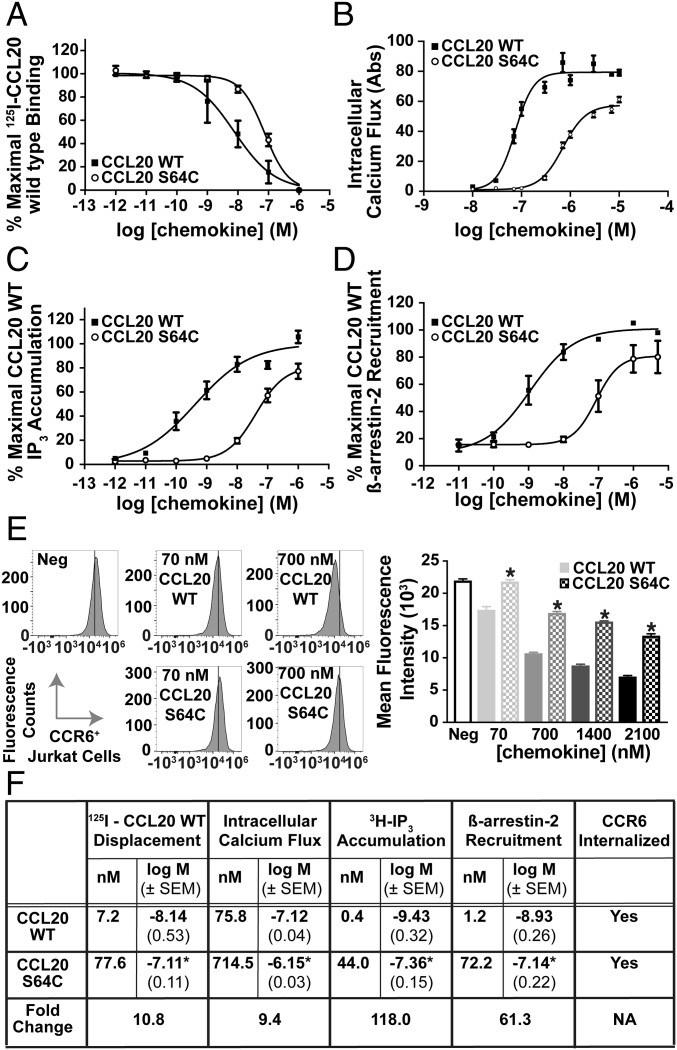
Fig. 2.
Biochemical characterization of CCL20 S64C activation of CCR6. (A) Binding of CCL20 proteins was observed by 125I-CCL20 WT displacement from CCR6+ transfected COS-7 cells. The Kd values for CCL20 WT and S64C binding to CCR6 were calculated as 7.2 nM (n = 4) and 77.6 nM, respectively (n = 3). (B) Administration of CCL20 WT and S64C on CCR6+ Jurkat cells promoted intracellular calcium release with EC50 values of 75.8 and 714.5 nM, respectively (n = 3). (C) Accumulation of 3H-IP3 was determined by radioactive measurements on transfected CCR6+ COS-7 cells in response to CCL20 WT and S64C with resulting EC50 values of 0.4 and 44.0 nM (n = 4). (D) Dose-dependent treatment of U2OS cells with CCL20 WT and S64C promoted β-arrestin-2 recruitment to CCR6 with EC50 values of 1.2 nM (n = 5) and 72.2 nM (n = 4). (E) Treatment with CCL20 S64C reduced CCR6 cell surface expression less efficiently than CCL20 WT. *P < 0.05 vs. same WT group (n = 2). (F) Table, summary of experimental EC50 values, corresponding logEC50 ± SEM, and receptor internalization results. *P < 0.05 vs. CCL20 WT group.