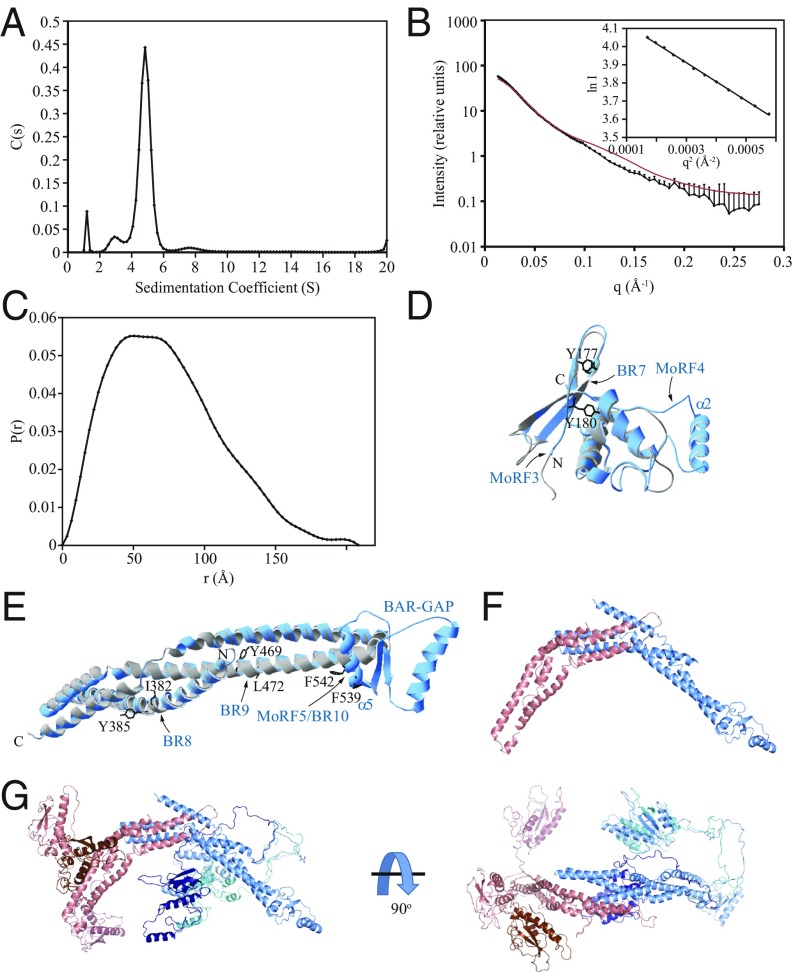
Fig. 5.
Structural characterization of Atg20. (A) Sedimentation velocity AUC recorded on the full-length Atg20-Snx4 heterodimer. (B) In-line SEC with SAXS data recorded on the Atg20156–640-Snx421–423 heterodimer. (Inset) The Guinier region for these data. SAXS data calculated from the Atg20-Snx4 ensemble homology model in F are shown in red. (C) Pair distance distribution function calculated from the SEC-SAXS data in B. (D and E) Homology modeling of structurally stable domains in Atg20. (D) Structural alignment of the crystal structure of the PX domain of SNX1 (gray) with the homology model of the PX domain of Atg20 (blue). (E) Structural alignment of the crystal structure of the BAR domain of SNX1 (gray) with the homology model of the BAR domain of Atg20 (blue). The amino acid residues of Atg20 mutated to Glu (Tyr177, Tyr180, Ile382, Tyr385, Tyr469, Leu472, Phe539, and Phe542) are shown (black). Phe539 and Phe542 are within MoRF5/BR10 that maps on the putative α5 helix of the BAR-GAP. (F) Atg20-Snx4 homology model of the BAR domain dimer. Atg20 is shown in blue; Snx4, in red. (G) Atg20-Snx4 ensemble model generated using BilboMD. The BAR domains of the different ensemble models are superimposed. The PX domain and linker from each model are shown in a different shade of blue (Atg20) or red (Snx4).