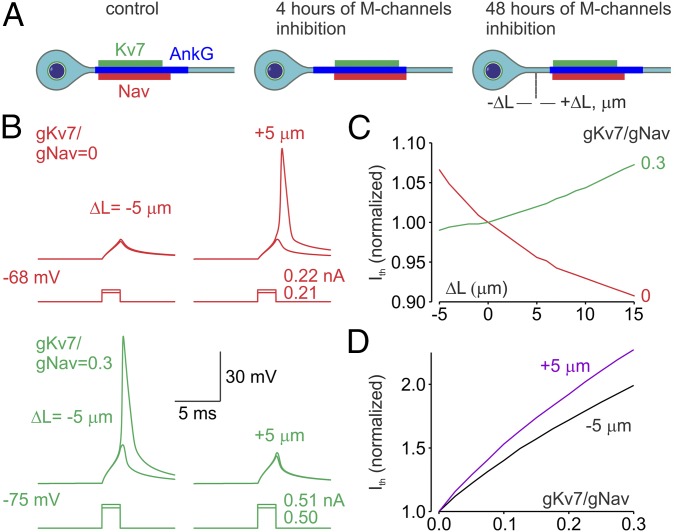
Fig. 8.
Functional implications of the distal relocation of the Nav and Kv7 channels. (A) Schematic drawing of the effect of short- and long-term M-channel inhibition on the distribution in the AIS of Nav (red) and Kv7 (green) channels and ankyrin G (blue). Notice that after relatively short periods of M-channel inhibition the Nav and Kv7 channels relocate away from the soma [relocation (ΔL) is expressed in micrometers]. This rapid channel relocation readjusts neuronal excitability. If M-channel inhibition persists for days, the ankyrin G segment also relocates away from the soma. (B) Simultaneous distal relocation of the AIS Nav and Kv7 channels causes a decrease in neuronal excitability. (Upper) In a model in which 35-μm-long AIS contains Na+ channels (2,000 pS/μm2, red traces) but no Kv7 channels, brief somatic current steps with amplitude of less than 0.22 nA fail to elicit an AP following the proximal AIS relocation (ΔL = −5 µm) from the initial position of 10 µm, but they elicit APs following the distal AIS relocation (ΔL = +5 μm). (Lower) In a model in which AIS also contains Kv7 channels at density 0.3 times of of the Nav channels (green traces), a current step with an amplitude of 0.51 nA elicits an AP when ΔL = −5 μm, but it fails to do so at ΔL = +5 μm. (C) The effect of AIS relocation on current threshold depends on the gKv7:gNav ratio. Distal relocation of the AIS containing only Na+ channels (gKv7:gNav ratio = 0, red trace) causes a decrease in the current threshold. The current threshold increases as a function of L when the gKv7:gNav ratio is equal to 0.3 (green trace). Shown are the current threshold values normalized to current the threshold for the initial AIS position at distance of 10 µm from the soma (ΔL = 0). (D) Varying effects of Kv7 channel density on the current threshold are dependent on the channel position within the AIS. In a model with constant Na+ channel density, raising gKv7 is more effective in modulating current threshold when the AIS is relocated away from soma (purple trace, ΔL = +5 µm) than when it is relocated toward the soma (black trace, ΔL = −5 µm).