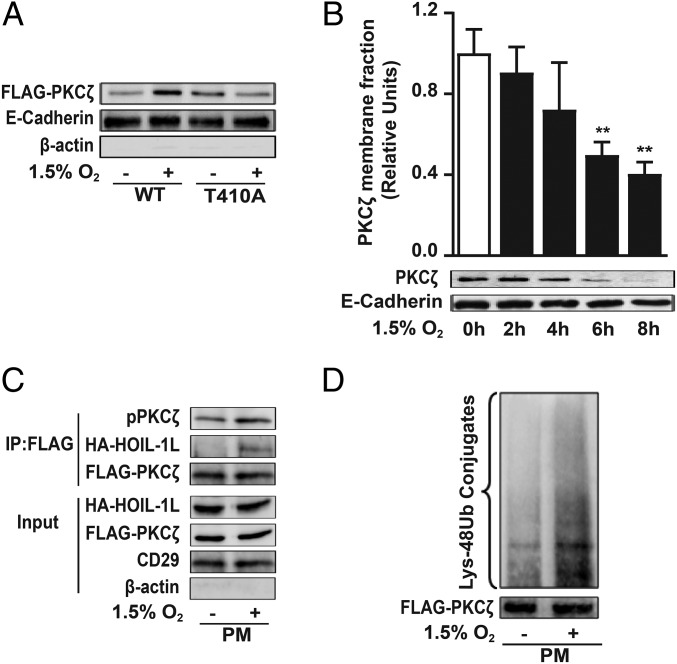
Fig. 6.
PKCζ degradation is initiated at the cell plasma membrane. (A) COS-7 cells were transfected with FLAG-WT-PKCζ (WT) or FLAG-T410A-PKCζ (T410A) and exposed to 1.5% O2 for 10 min, and pPKCζ levels in the isolated plasma membrane fraction were determined by Western blot to assess PKCζ translocation to the plasma membrane as described in SI Appendix, SI Experimental Procedures. E-cadherin was used as loading control for membrane fraction, and β-actin was used as a marker of cytosolic proteins. Representative immunoblots from four independent experiments are shown. (B) Isolated plasma membrane proteins from rat ATII cells exposed to normoxia or 1.5% O2 were immunoblotted using an anti-PKCζ antibody. E-cadherin was used as loading control (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA and the Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (**P < 0.01). (C) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with FLAG-WT-PKCζ (WT) and HA-HOIL-1L; after 4 h of normoxia or 1.5% O2 exposure, plasma membrane proteins were isolated and used for coimmunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted for pPKCζ and HOIL-1L. FLAG was used as a loading control. β-Actin and CD29 are shown as loading controls for cytosolic and membrane fraction, respectively. Representative immunoblots from at least three independent experiments are shown. (D) PKCζ ubiquitination was evaluated in COS-7 cells transfected with FLAG-PKCζ-WT. After 4 h of hypoxia, an immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody was performed in isolated plasma membrane and immunoblotted for Lys-48 poliubiquitylation. Representative immunoblots from at least three independent experiments are shown.