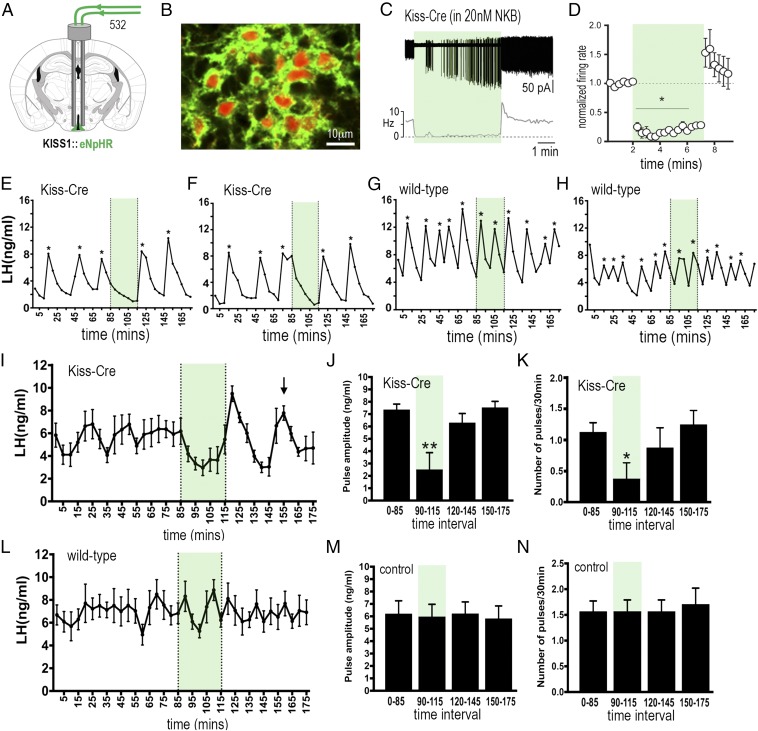
Fig. 4.
Halorhodopsin inhibition and activation of ARNKISS neurons suppresses and then initiates ongoing pulsatile LH secretion in gonadectomized female mice. (A) KISS1-Cre mice injected with Cre-dependent eNpHR3.0-eYFP AAV into the ARN (green) and implanted with bilateral optic fibers in the ARN. (B) Dual fluorescence image of ARNKISS neurons expressing eNpHR3.0 (green) and kisspeptin (tdTomato reporter). (C) Action potential firing in an eNpHR3.0-expressing ARNKISS neuron in the presence of 20 nM NKB. The neuron responds to green light with an abrupt decrease in firing followed by a sharp rebound activation immediately after the light is stopped. (C, Top) Action potential firing. (C, Bottom) Rate meter. (D) Mean (±SEM) normalized firing rate of ARNKISS neurons (n = 6) responding to green light. *P < 0.05 compared with baseline, Friedman test. (E–H) Pulsatile LH secretion in eNpHR3.0 KISS1-Cre (E and F) and wild-type (G and H) gonadectomized female mice. Green light illumination is indicated by green shading and LH pulses are indicated by asterisks. (I) Mean (±SEM) LH levels in KISS1-Cre mice (n = 8) showing the suppression of LH secretion during green light illumination and the subsequent rebound of LH and resetting of the pulse generator to evoke a subsequent LH pulse in all mice (arrow). (J and K) Mean (±SEM) LH pulse amplitude and pulse frequency before (0 to 85 min), during (90 to 115 min; green shading), and subsequent to (120 to 145 and 150 to 175 min) green laser illumination. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus 0 to 85 min, ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s test; n = 8. (L–N) Basal (±SEM) LH levels and LH pulse amplitude and frequency in control AAV-injected wild-type mice (n = 7).