Figure 5.
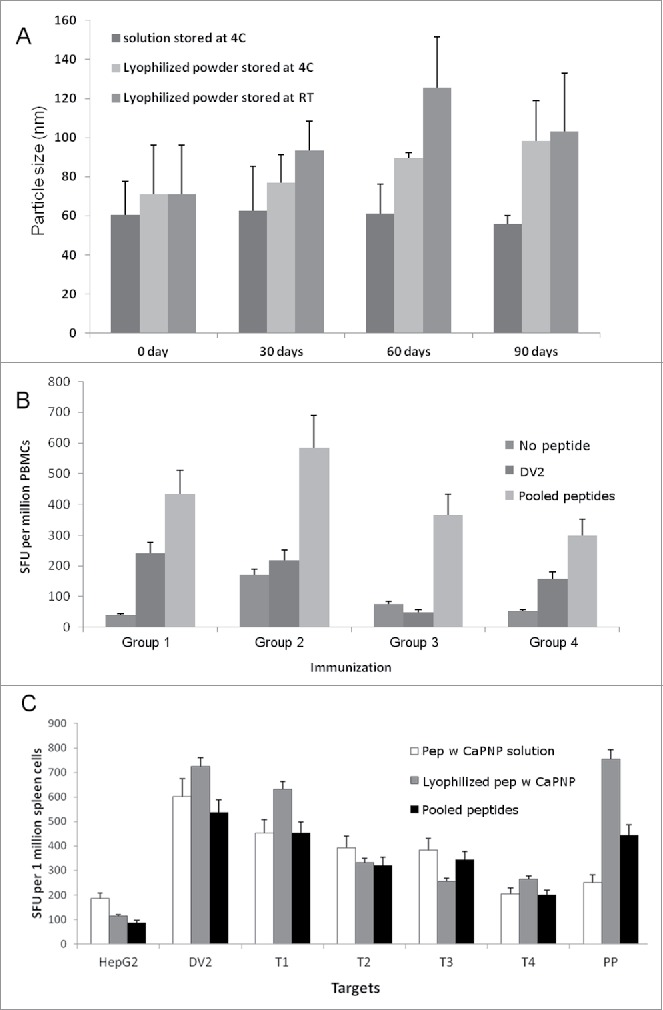
Stability and efficacy of CaPNP/multipeptide formulation. (A) Formulation integrity as measured by particle size over a time of 3 months (days 0, 30, 60 and 90) under different storage conditions (4°C or RT). Data represented as mean ± SD (n = 3) of particle size. (B) Using PBMCs, in vitro CTL responses to formulations in varied storage conditions were generated. Four groups were tested: 1) pooled peptide emulsified in ISA 51; 2) CaPNP/multipeptide formulation with GlcNAc stored at 4°C; 3) lyophilized CaPNP/multipeptide formulation with GlcNAc stored at 4°C; or 4) lyophilized CaPNP/multipeptide formulation with GlcNAc stored at RT. CTL responses were assessed by co-culturing stimulated PBMCs with HepG2 targets that were pulsed with no peptide, or pooled peptides, or infected with DV2. IFNγ expression was measured by ELISpot assay. Data represented as mean ± S.D (n = 3) of SFU per 1 million PBMCs. (C) Using HLA-A2+ transgenic mice, in vivo CTL responses to varied storage conditions were generated. Three groups were tested: 1) pooled peptide emulsified in ISA 51, 2) CaPNP/multipeptide formulation with GlcNAc stored at 4°C, or 3) lyophilized CaPNP/multipeptide formulation with GlcNAc stored at 4°C. Mice were immunized as described in Fig. 1A. CTL responses were assessed by co-culturing splenocytes with HepG2 targets that were either no peptide (HepG2), or pulsed with pooled peptides, or infected with DV2, or infected with Thai isolates of 4 different DV serotypes (Thai isolates of DV serotype-1 [T1], -serotype 2 [T2], -serotype 3 [T3], -serotype 4[T4]). Data represented as mean ± S.D (n = 3) of SFU per 1 million splenocytes.
