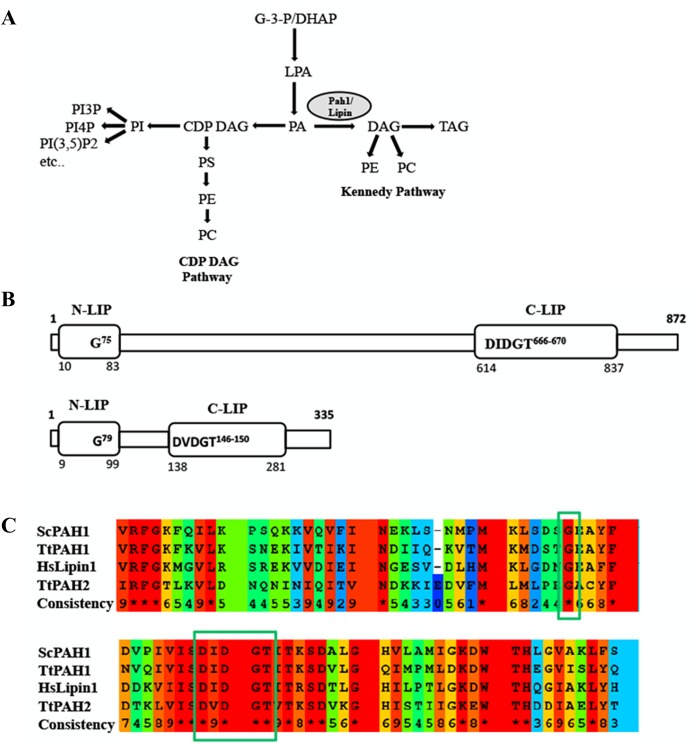
Fig. 1.
Domain organization, sequence analysis and function of PAH protein. (A) Schematic representation of the role of PAH in lipid biosynthesis. PA is a key precursor used for the synthesis of PE and PC through the CDP-DAG pathway. In the presence of choline and ethanolamine, these phospholipids are synthesized through the Kennedy pathway. In metazoans, the pathway that converts CDP-DAG to PC/PE (CDP-DAG pathway) does not exist, whereas both the pathways are present in yeast. G-3-P, glycerol-3-phosphate; LPA, lysophosphatidate; PI3P, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate; PI4P, phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate; PI(3,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol-3, 5-biphosphate; PS, phosphatidylserine. (B) Domain organization of TtPAH1 and TtPAH2. Predicted N-LIP and C-LIP domains are indicated in the boxes. Also shown are the positions of a conserved glycine residue in N-LIP and the HAD with its conserved DXDXT/V motif in C-LIP. (C) Multiple sequence alignment showing partial sequences of N-LIP (top) and C-LIP (bottom) of PAH proteins from T. thermophila, S. cerevisiae and H. sapiens. Assigned colors of the particular residues are based on alignment consensus. Conserved glycine residue in N-LIP and catalytic motif (DXDGT/V) in C-LIP are indicated inside the box.