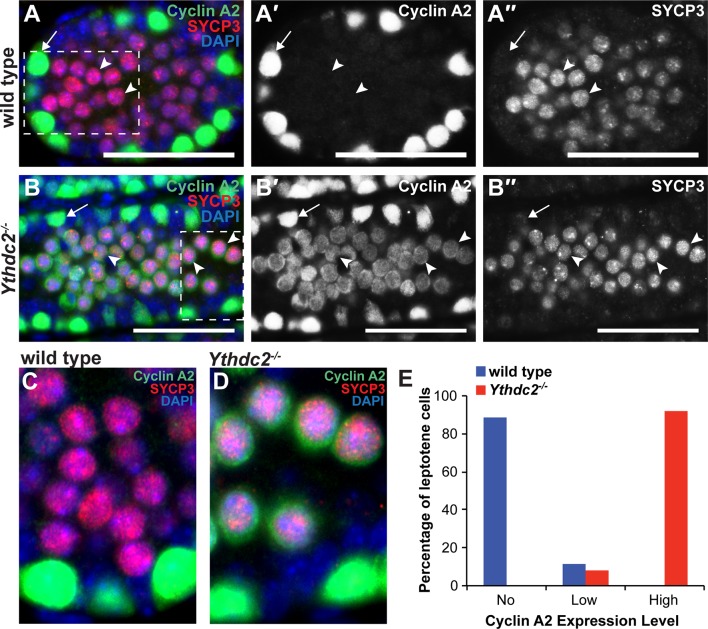
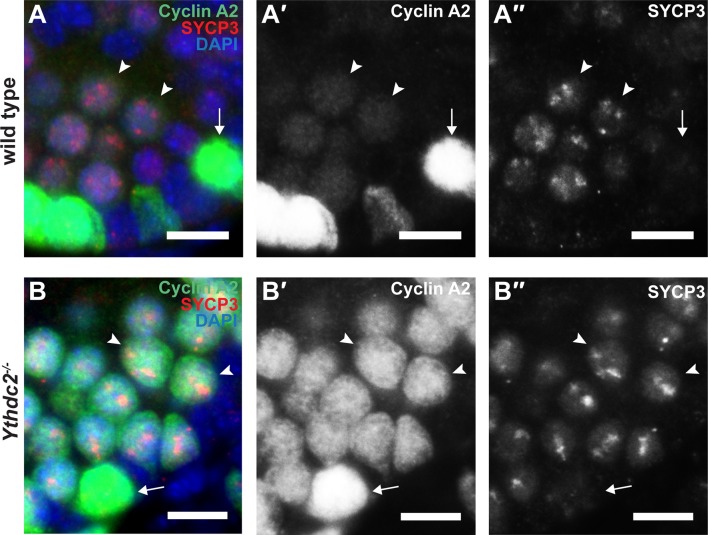
Figure 7. YTHDC2-deficient meiotic germ cells fail to turn off expression of Cyclin A2.
(A-B′′) Immunofluorescence images of testis cross-sections from P12 (A-A′′) wild-type and (B-B′′) Ythdc2-/- mice stained in parallel for Cyclin A2 (green), SYCP3 (red) and DAPI (blue). Arrow: spermatogonia. Arrowheads: leptotene spermatocytes. Scale bars: (A-B′′) 50 μm. (C) High magnification of boxed region in panel A. (D) High magnification of boxed region in panel B. (E) Quantification of Cyclin A2 protein expression levels in leptotene spermatocytes in P12 wild-type (blue) or Ythdc2 mutant (red) testes (counted leptotene spermatocytes from n = 3 wild-type and n = 3 Ythdc2-/- mice; >365 leptotene spermatocytes counted for both wild-type and Ythdc2-/- mice). See also Figure 7—figure supplement 1 and Figure 7—source data 1.