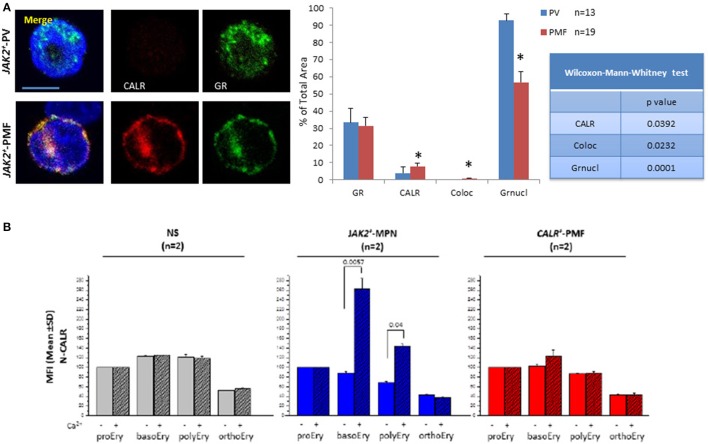
Figure 5.
The JAK2V617F mutation abrogates the association between CALR and the glucocorticoid receptors in patients with Polycythemia Vera. It also makes the mutant erythroid progenitors capable to up-regulate the cell surface expression of CALR in response to Ca2+. (A) Single and merged confocal microscopy observations of a representative erythroid progenitor cell expanded in culture from patients with JAK2+ Polycythemia Vera (PV) and Primary Myelofibrosis (PMF) stained with antibodies against C-CALR (red) or the glucocorticoid receptor (green), as indicated. Merged areas are in yellow. Nuclei were counterstained in blue with DAPI. Original magnification: 1,200x. The bar corresponds to 10 μm. The results with PV are similar to those published in (Falchi et al., 2017). The results with PMF are not published and were obtained in experiments conducted in parallel with those on PV. Technical details are provided in and are also shown in Figure 2. *Indicates values statistically different (p < 0.05) between PV and PMF. (B) Levels of N-CALR detected by flow cytometry on the cell surface of erythroid cells expanded in vitro from non-diseased donors (ND, 2 different subjects) or from patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms carrying either the JAK2V617F or the Type 2 CALR+ mutation (2 patients in each group) and treated in vitro for 2 h with EPO in the presence of either Ca2+-depleted or Ca2+-supplemented phosphate buffered saline. Results are expressed as Mean Fluorescence intensity (MFI) obtained in separate experiments performed in duplicate. Erythroid cells were divided into classes of progressive maturation (proerythroblasts, basophilic, polychromatophilic, and orthochromatic erythroblasts) according to established flow cytometry criteria based on CD36 and CD235a staining (Migliaccio et al., 2011). The levels of cell surface expression of N-CALR between cells exposed or not to Ca2+ is statistically different (by Anova) only for erythroid cells harboring the JAK2 mutation. The results of the cells not treated with Ca2+ were already published in Falchi et al. (2017). The technical details of these experiments are provided in Falchi et al. (2017).