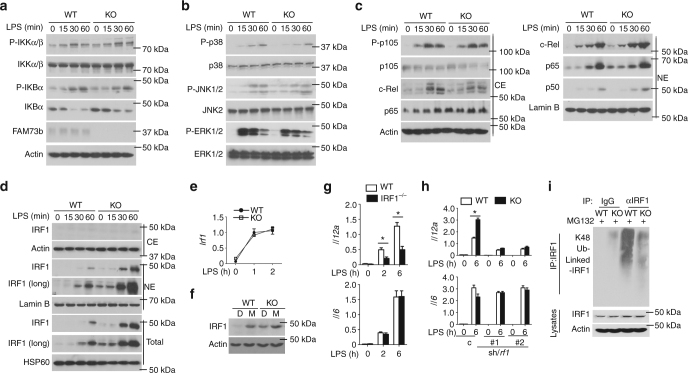
Fig. 5.
FAM73b deficiency promotes IRF1 stability. a–c The indicated proteins in whole-cell lysates (a, b) or cytoplasmic (CE) and nuclear (NE) extracts (c) of WT and FAM73b KO BMDMs were measured by IB analysis. d IB analysis of the IRF1 level in LPS-stimulated WT or FAM73b KO BMDMs. qRT-PCR analysis of Irf1 in WT or FAM73b KO BMDMs (e). IB analysis of the IRF1 levels in BMDMs after pretreatment with DMSO or MG132 for 30 min before harvest (f). g Il12a and Il6 mRNA levels were evaluated by qRT-PCR. h WT and FAM73b KO BMDMs infected with pGIPZ lentiviral vectors encoding a non-silencing control shRNA (C) or two different Irf1-specific shRNAs. qRT-PCR analysis of the indicated genes. The data are presented as the fold-induction relative to the Actb mRNA level. i WT and FAM73b KO BMDMs were stimulated with LPS for 60 min and incubated with MG132 for 30 min. IRF1 was isolated by IP (under denaturing conditions), and its ubiquitinated form was detected by IB using anti-K48-linked ubiquitin antibody. Protein lysates were also subjected to direct IB (bottom panels). Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. Two-tailed unpaired t-tests were performed; *P < 0.05