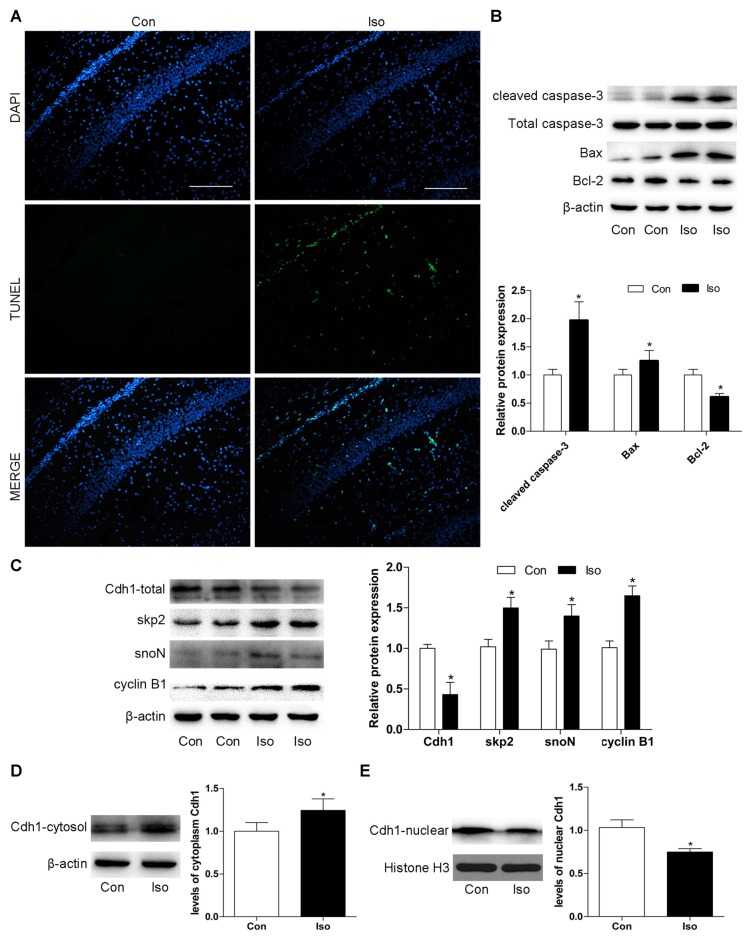
Figure 1.
Exposure to isoflurane downregulates Cdh1 activity and induces neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus of postnatal 7-day rat pups. Anesthesia was induced by placing rats at postnatal day 7 (P7) in an anesthetizing chamber prefilled with 30% oxygen (O2) and 70% nitrogen (N2) in the absence or presence of 2% isoflurane for 6 h. (A) After isoflurane exposure, apoptosis of hippocampal neurons was assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dutp nick end labeling (TUNEL)-assay. TUNEL-positive cells are labeled in green; blue, nuclei stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Scale bar = 200 μm. (B,C) After isoflurane-treatment, rat hippocampal tissues were collected to assess the expression of apoptosis-related proteins (cleaved caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2), total Cdh1 and several downstream substrates (skp2, snoN and cyclin B1) by western blotting. Quantitative data for the western blot (n = 3 for each group) are shown by histograms. β-actin was set as an internal reference, and the fold change for density in the control group was used for quantification. (D,E) Representative levels of Cdh1 in the cytosol and nucleus. The histogram represents the quantitative analysis (n = 3 in each group). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *P < 0.05 vs. control group.