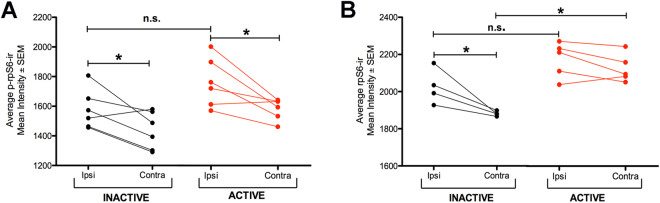
Figure 7.
Effects of STN DBS on Phosphorylated and Total Levels of rpS6. Quantification of the Inactive and Active groups was assessed between hemispheres and treatments to determine the effect of stimulation on p-rpS6 (A) and rpS6 (B). (A) THir SN neurons expressing hu-α-syn exhibited significantly more p-rpS6 immunoreactivity (Inactive, n = 6: t(5) = 2.805, p = 0.0378; Active, n = 6: t(5) = 3.040, p = 0.0287). However, p-rpS6 appeared to increase slightly within α-syn expressing THir SN neurons in association with stimulation, whereas STN DBS overall had no significant impact on p-rpS6 immunoreactivity in either the ipsilateral or contralateral SNpc (F(3,22) = 5.715, p > 0.05). (B) Total rpS6 was significantly increased in THir SN neurons expressing hu-α-syn in Inactive rats (n = 4; p = 0.0491) but not in Active Rats (n = 6; p > 0.05). Active STN DBS did not affect rpS6 immunoreactivity in hu-α-syn expressing neurons (p > 0.05) but did increase rpS6 immunoreactivity in the contralateral SNpc THir neurons (p = 0.004).