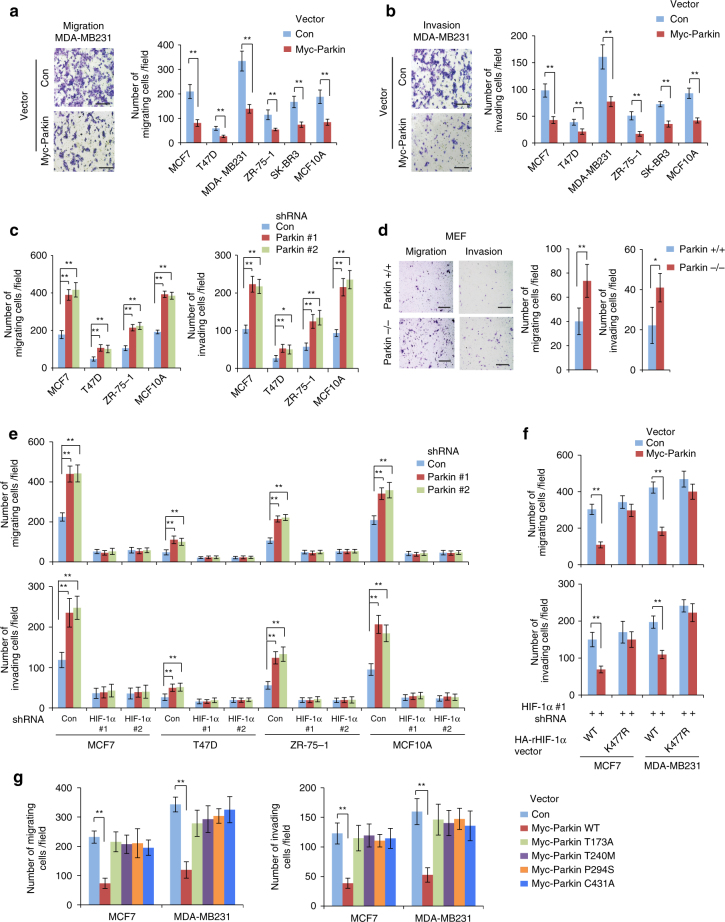
Fig. 6.
Parkin inhibits migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells through negative regulation of HIF-1α. a, b Myc-Parkin expression inhibited the migration (a) and invasion (b) of different human breast cells as determined by transwell assays. Left panels of a, b: representative images of migrating (a) or invading (b) MDA-MB231 cells transduced with control (Con) or Myc-Parkin vectors. Scale bars: 200 μm. Right panels of a, b: quantification of average number of migrating or invading cells per field. c Knockdown of endogenous Parkin by shRNA vectors promoted the migration and invasion of different human breast cells. d Parkin−/− MEFs displayed enhanced abilities of migration and invasion compared with Parkin + / + MEFs. Left panel: representative images of migrating or invading cells. Scale bars: 500 μm; Right panel: quantification of average number of migrating or invading cells per field. e Knockdown of HIF-1α largely abolished the promoting effect of Parkin knockdown on migration (upper panel) and invasion (lower panel) of cells as measured by transwell assays. Cells with HIF-1α knockdown were further transduced with control or Parkin shRNA vectors for transwell assays. f Expression of K477R HA-rHIF-1α largely abolished the inhibitory effect of Myc-Parkin on cell migration (upper panel) and invasion (lower panel) in MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cells. Endogenous HIF-1α in cells was replaced with WT or K477R HA-rHIF-1α (shown in Fig. 5g), and cells were then transduced with Myc-Parkin for transwell assays. g C431A, T173A, T240M and P294S mutations of Parkin compromised the inhibitory effects of Parkin on cell migration (left panel) and invasion (right panel). In a–g, the data present mean ± SD (n = 6). #: P < 0.05; *P < 0.01; **P < 0.001; two-tailed Student’s t test