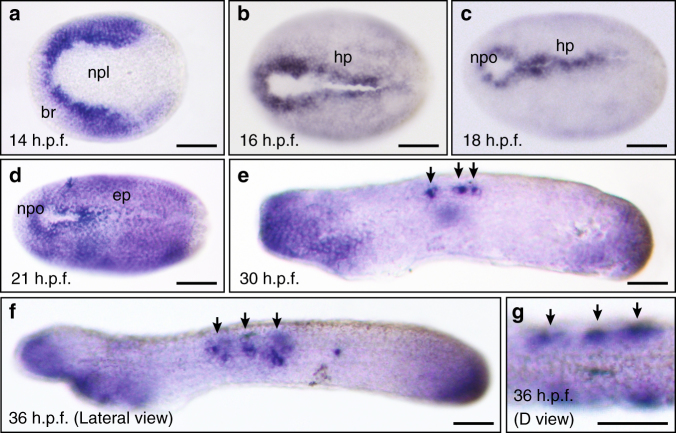
Fig. 3.
Esrp is expressed dynamically in the non-neural ectoderm during amphioxus embryo development. WMISH of Esrp in Branchiostoma lanceolatum embryos. Anterior is to the left in all cases. a 14 h.p.f. early neurula (dorsal view) showing expression in the ectodermal cells located in the border region (br) next to the neural plate (npl). b, c 16 h.p.f. and 18 h.p.f. mid-neurula embryos (dorsal view) stained most strongly in the ectodermal cells next to the neural plate border and that form the hinge points (hp) during neural tube closure. The location of the neuropore (npo) is indicated. d In 21 h.p.f. late neurula (dorsal view), Esrp expression is extended throughout the whole epidermis (ep). e, f Early (30 h.p.f.) and late (36 h.p.f.) pre-mouth stages (lateral views) showing Esrp-positive cells in anterior ectoderm, tailbud epithelia and in a few cells that likely corresponding to migrating sensory cells during epidermal incorporation or already integrated into the epithelium (black arrows). g Dorsal view of a 36 h.p.f. embryo shows the epidermal location those Esrp-positive cells (black arrows). Scale bars: 50 µm a–f, 25 µm g