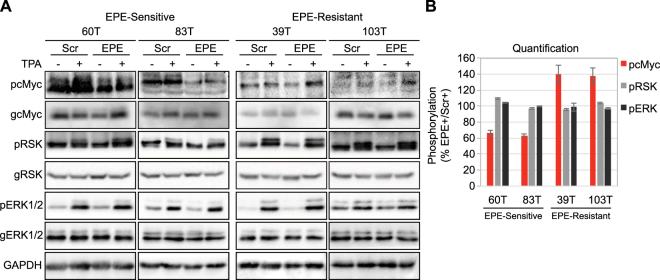
Figure 3.
The EPE peptide reduces phosphorylation of nuclear targets in NRAS mutant melanomas. Two NRAS melanomas sensitive to EPE peptide (60T an 83T), and two EPE-resistant melanomas (39T and 103T), were serum starved (16 h), pretreated with EPE or Scr peptides (10 µM, 2 h), and stimulated with TPA (100 nM, 15 min) (+) or left untreated (−). Cell lysates where analyzed by WB using the indicated antibodies. (A) (Left) In the EPE-sensitive cells, the peptide reduced the phosphorylation of nuclear target c-Myc in stimulated and basal state, while not affecting cytosolic target RSK. (Right) In EPE-resistant cells, the peptide had no effect on the phosphorylation of RSK, and slightly increased levels of phospho-c-Myc. (B) Quantification of bands in (A). Bars represent average band density ratio of EPE stimulated samples (EPE+) compared to Scr stimulated samples (Scr+), ±S.E. of 2 or 3 independent experiments. Bands were quantified using ImageJ.