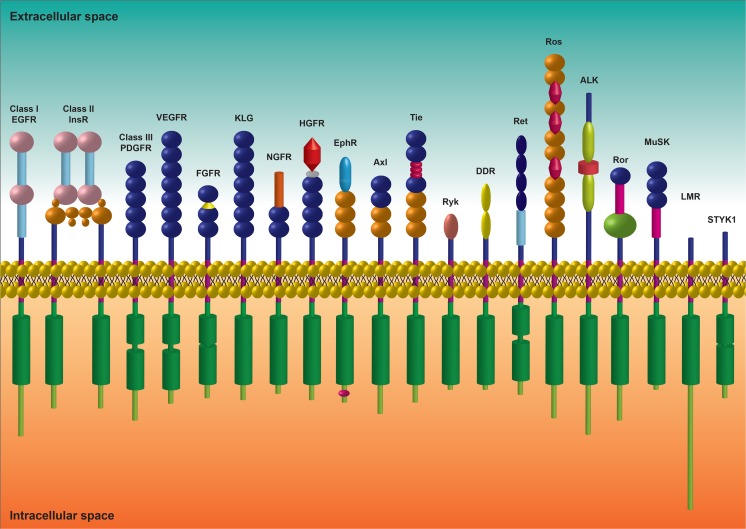
Fig. 1.
General structure of RTKs families. The extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular structural domains of the 20 families of human RTKs are represented schematically. Green cylinders represent the intracellular regions containing the kinase domains and purple rectangles show the transmembrane region. The main structural differences between all RTKs classes are located in the extracellular domain and confer ligand specificity. The classical EGFR, InsR and PDGFR families are also known as class I, class II and class III RTKs, respectively. c-KIT belongs to the class III, PDGFR family.  - L;
- L;  - cysteine-rich;
- cysteine-rich;  - fibronectin type III;
- fibronectin type III;  - immunoglobulin domain;
- immunoglobulin domain; 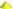 - acid box;
- acid box; 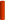 - leucine-rich;
- leucine-rich; 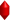 - sema;
- sema;  - psi;
- psi;  - ephrin binding domain;
- ephrin binding domain; 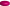 - EGF;
- EGF;  - WIF;
- WIF;  - discoidin;
- discoidin;  - cadherin;
- cadherin;  - YWTD propeller;
- YWTD propeller;  - mam domain;
- mam domain;  - Ldla;
- Ldla;  - fz;
- fz;  - kringle
- kringle