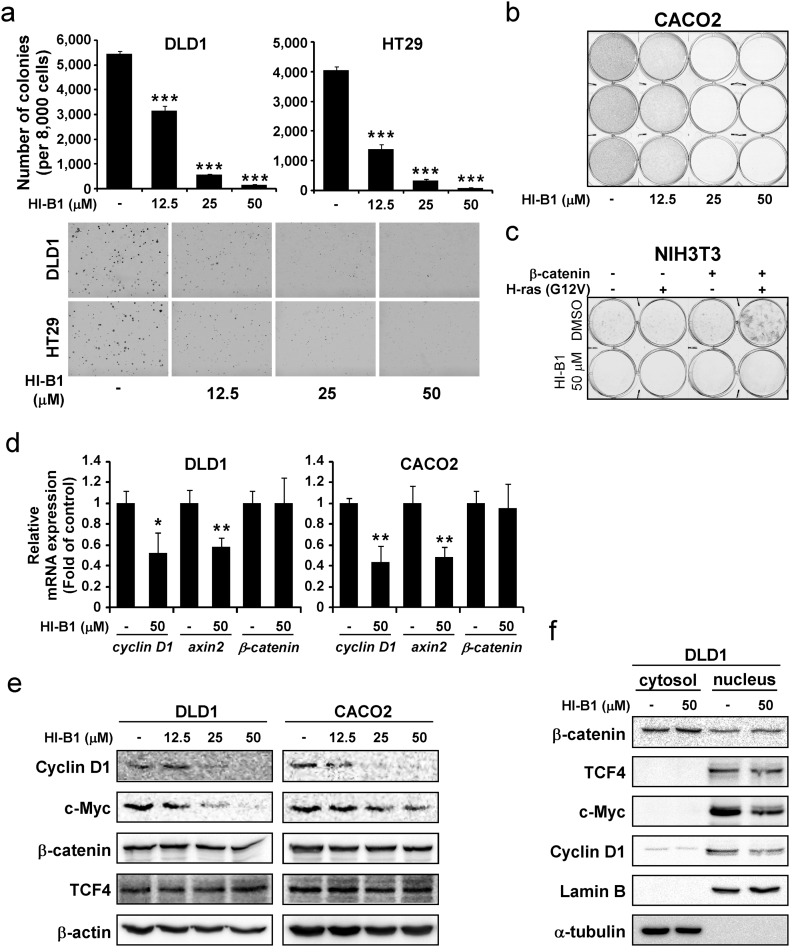
Fig. 2.
HI-B1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth by suppressing β-catenin activity.
(a) Cells were seeded into 0.3%-agar-containing medium with various concentrations of HI-B1 and the numbers of colonies was counted at Day 7.
(b) Cells were seeded on 6-well plates with various concentrations of HI-B1 and then stained with crystal violet solution at Day 7.
(c) Foci formation was induced by co-transfection of β-catenin and H-ras (H12V) in NIH3T3. After transfection, cells were treated with HI-B1 and stained with crystal violet solution (Day 14). The medium was changed every other day.
(d and e) After 24 h of HI-B1 treatment, mRNA (d) and protein (e) were harvested from the cells and relative amount was measured by qRT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively.
(f) The cytosol and the nucleus portions of the cells were fractionated at 24 h of HI-B1 treatment. Lamin B and α-tubulin were used as a cytosol and a nucleus marker, respectively.
All values of graphs present mean ± SD (in triplicate). Significant differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA compared with DMSO-treated group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).