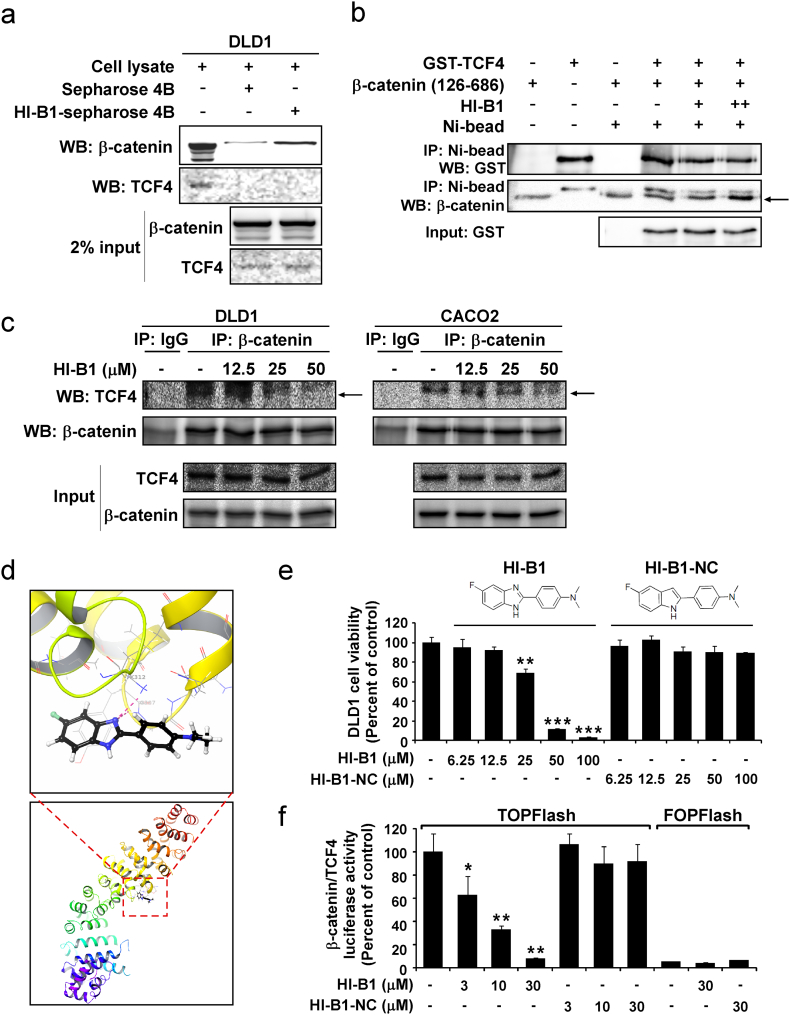
Fig. 3.
HI-B1 directly targets β-catenin and disrupts β-catenin/TCF4 complex formation.
(a) HI-B1 directly binds with β-catenin. HI-B1 was conjugated with Sepharose 4B beads and incubated with cell lysates. Protein co-immunoprecipitated with the beads was analyzed by Western blotting.
(b) HI-B1 disrupts the formation of the β-catenin/TCF4 complex in vitro. His-tagged β-catenin (126–686) was immunoprecipitated with nickel beads and the amount of TCF4 was detected by Western blotting.
(c) DLD1 and CACO2 cell lysates were harvested after 24 h of HI-B1 treatment. β-Catenin was immunoprecipitated and binding proteins was detected by Western blotting.
(d) Molecular docking predicts the interaction of HI-B1 and β-catenin. A nitrogen atom of HI-B1 forms a hydrogen bond with β-catenin (upper panel) from Extra precision (XP) docking in silico (lower panel).
(e and f) HI-B1 and HI-B1-NC (a nitrogen atom was substituted with a carbon) were treated to DLD1 cells (n = 3). Proliferation was measured by MTS assay at 48 h (e), and β-catenin/TCF4 luciferase activity was measured by luminometer at 24 h (f). Significant difference with DMSO-treated group by One-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).