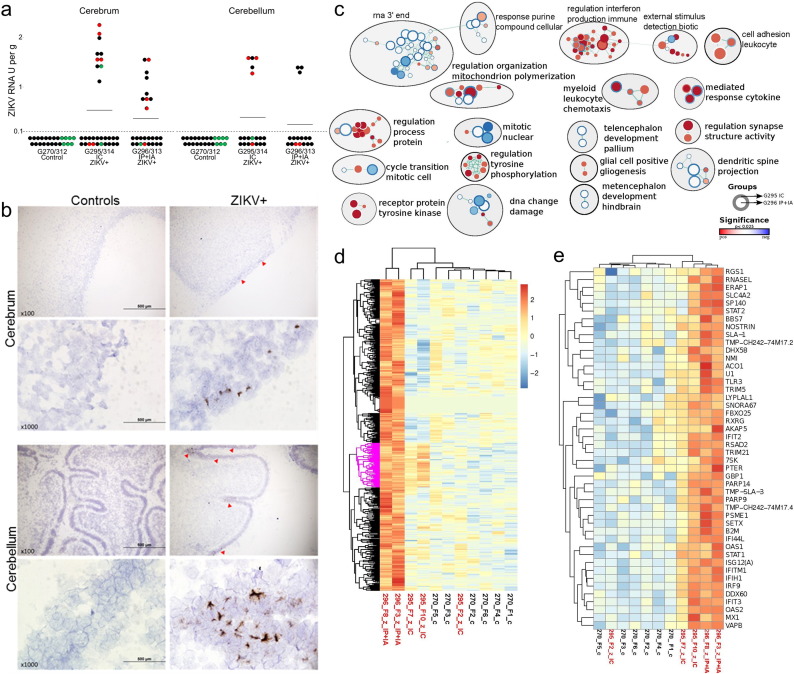
Fig. 4.
ZIKV infection and molecular pathology in fetal brains. (a) PCR titers in the cerebrum and cerebellum. A dotted line represents the assay detection limit. Dots below the detection limit are negative samples. Green dots represent fetuses directly mock-inoculated IC or IP + IA. Red dots represent fetuses directly inoculated with ZIKV IC or IP + IA. Black dots represent non-manipulated fetuses. Dots with yellow demarcations represent samples positive for ZIKV RNA by in situ hybridization. Two fetuses (9%) out of 23 tested by ISH had virus RNA in the cerebral cortex. Two fetuses (15%) out of 13 tested by ISH had virus RNA in the cerebellar cortex. (b) ZIKV-specific in situ hybridization staining in the fetal cerebrum and cerebellum. Brown staining indicates ZIKV RNA. Control samples from mock-exposed fetuses and tissues from ZIKV-exposed fetuses treated with ZIKV-specific and negative control probes, respectively, had no staining. Red arrowheads indicate regions with ZIKV RNA. (c) Combined enrichment map of GO biological process terms with significant positive or negative association to treatment groups. Circles represent gene sets with the outer ring representing fetuses from the intracerebral (IC) group (G295 IC) and the inner ring representing fetuses from the intraperitoneal + intra-amniotic (IP + IA) group (G296 IP + IA). White space in the inner or outer rings indicates no significant enrichment. All nodes had a p-value of < 0.025. The circle size is scaled to the number of genes in the gene set and colour is scaled to the p-value. The green lines indicate shared genes between the gene sets. Gene sets with either increased or decreased enrichment are in red and blue respectively. Subnetworks related to immunity are organized top right; neuro related subnetworks are bottom right; the left is cell signalling, division and metabolism subnetworks. (d) Heatmaps of the 669 genes with FDR corrected p-value < 0.05 were clusters by hierarchical clustering. Gene sets with either increased or decreased enrichment are in red or blue respectively. There was a small group of co-up-regulated genes, although with weaker expression in the IC exposed fetuses (pink highlighted group). This small set of genes was significantly enriched in a number of GO pathways related to virus, defense, immune, interferon, and stress responses (Dataset S2 – Sheet 4). G270 is a control litter. x and y axes represent, respectively, sample identification and genes. (e) A zoomed view of the co-up-regulated group (pink highlighted group in d).