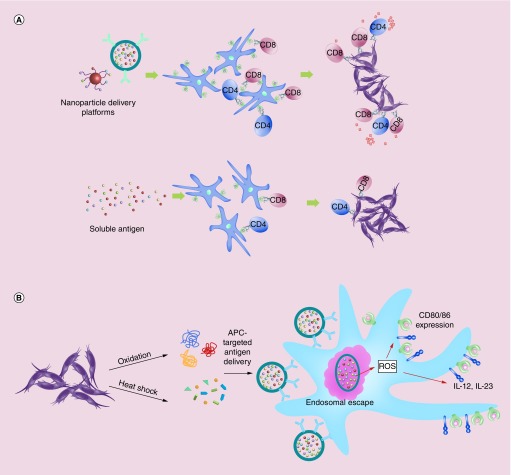
Figure 1. . Methods for enhancing antigen uptake and presentation for cancer immunotherapies and vaccines.
(A) Tumor antigen delivery via nanoparticles creates APC antigen depots and increases antigen presentation. Nanoscale platforms may be used in both settings to increase antigen uptake and presentation by MHC class I and II molecules, subsequently activating both CD8+ and CD4+ T cells for antitumor immunity, respectively. (B) Protein modification through oxidation or heat shock enhances antigen uptake and as well as APC activation. Antigens taken up by APCs that escape the endosome are more efficiently cross-presented. This may activate ROS, thus driving activation of APCs. Exogenous and codelivered TLR agonists as well as DAMPs and ligands for pathogen-activated recognition receptors contribute to APC activation and maturation, which can then upregulate costimulatory molecules and cytokine expression.
APC: Antigen-presenting cell; DAMP: Damage-associated molecular pattern; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TLR: Toll-like receptor.