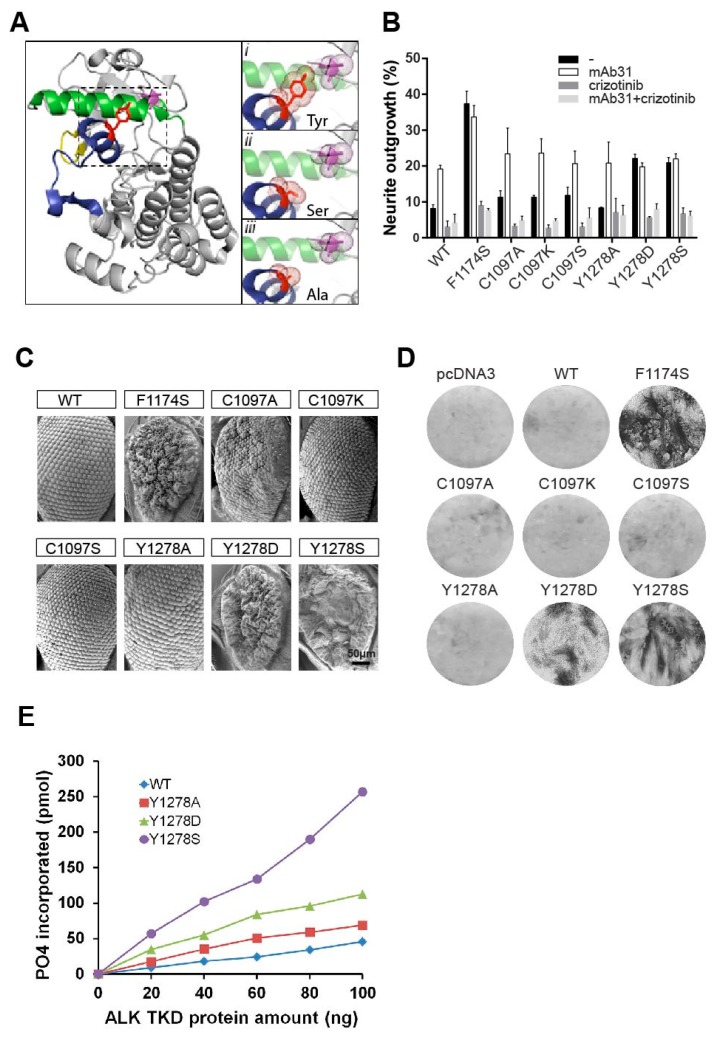
Figure 3.
Importance of the Y1278-C1097 hydrogen bond for ALK kinase domain regulation. (A, left panel) Structure depicting the ALK kinase domain. αC helix: green; activation loop: dark blue; glycine rich P-loop: yellow. Residues C1097 and Y1278 are shown in purple and red sticks respectively. Image was generated with PyMOL (DeLano Scientific, Palo Alto, CA, USA) using PDB: 3LCT. (Ai, inset) A close up view of the hydrogen bond between Y1278 and C1097. This hydrogen bond is absent when Y1278 is mutated to serine (Aii, inset) or to alanine (Aiii, inset). The selected side chains of residue 1278 (Y/S/A) and C1097 are shown in dotted balls and sticks; (B) Neurite outgrowth assay of PC12 cells expressing. Black bars represent untreated cells, white bars denotes cells stimulated with mAb31, dark grey indicate cells treated with 250 nM crizotinib, and light grey denote cells stimulated with mAb31 and treated with crizotinib together; (C) Scanning electron microscope images of Drosophila eyes ectopically expressing wild type ALK (ALK-WT) and mutant ALK variants (ALK-F1174S, ALK-C1097A, ALK-C1097K, ALK-C1097S, ALK-Y1278A, ALK-Y1278D, and ALK-Y1278S). ALK-F1174S was employed as positive control. Scale bar represents 50 μm; (D) Representative focus formation assays for NIH3T3 cells transfected with pcDNA3 empty vector, wild type ALK, or different mutant ALK variants as indicated; (E) In vitro kinase assay of the indicated ALK tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutants. Substrate phosphorylation activity of wild type ALK-F1174S, ALK-Y1278A, ALK-Y1278D and ALK-Y1278S was assayed employing a peptide mimic of the ALK activation loop. Increasing amounts of ALK TKD proteins were assayed at 30 °C for 30 min.