Fig. 3.
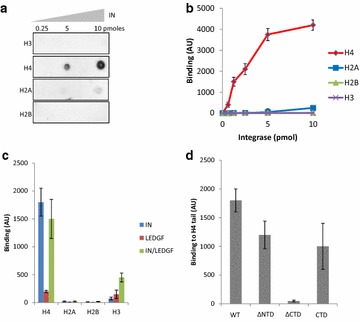
FAR dot-blot analysis of the interactions between HIV-1 IN and peptides derived from histones amino-terminal tails. The associations between IN and H3, H4, H2A and H2B biotinylated peptides from the histones tails (sequences in Figure S3) were evaluated using a far dot blot approach as described in the "Methods" section using 1 µl of 0.25 − 10 pmol of recombinant IN (lanes 0.25, 5 and 10) spotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and 1 µM of peptide H3, H4, H2A or H2B (a typical result is shown in a). The far dot blots were run three to ten times and the intensity of each spot was quantified using ImageJ software. The results are reported as the mean of the experiments ± standard deviation (b). Same experiments were conducted using IN, LEDGF/or the IN/LEDGF complex and results obtained with 2.5 pmol of the different proteins are reported in (c). The far dot blot assays were performed to identify the HIV-1 IN domain responsible for the recognition of the H4 histone tail. 2.5 pmol of truncated proteins lacking the NTD (∆NTD) or the CTD (∆CTD), or the isolated CTD (CTD), immobilized together with full-length WT IN were incubated with the H4 tail. Binding was quantified, and the results are represented as the mean of three to six independent experiments ± standard deviation in (d)
