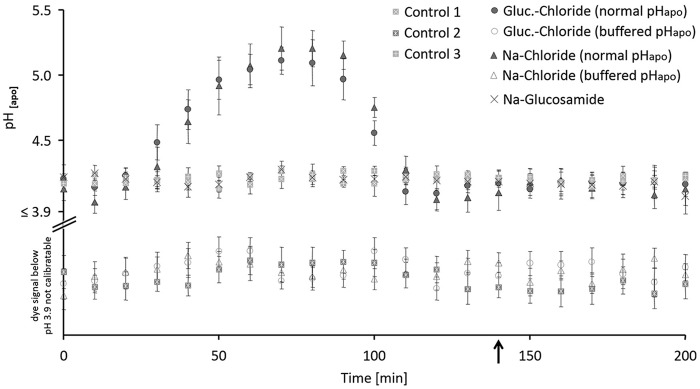
Figure 1.
In planta monitoring of leaf apoplastic pH shows that the formation of the transient alkalinization is inducible by the chloride component of NaCl stress. Plants were stressed with 50 mm of the salts, corresponding controls without salt. Chloride stress treatments are given as glucosamine (circle) or sodium chloride (triangle) under conditions when pHapo acted over its normal range (closed symbol) or when pHapo was clamped into the acid range at pH 3.7 (open symbol). Sodium glucosamide–treated plants are labeled by a cross and three different control groups (squares) guard the experiment against effects from the circadian rhythm or stress from the infiltration. Black arrow indicates the time point of taking leaf samples for the proteomics experiment, the cell wall extension assays, and the cell wall compound analysis. For pH measurement, 5 biological replicate samples were generated for each experimental group. Representative kinetic of one of the 5 biological replicates is shown. For this, pH quantitation was technically averaged with n = 6 regions of interest per ratio image and time point. Mean ± S.E.