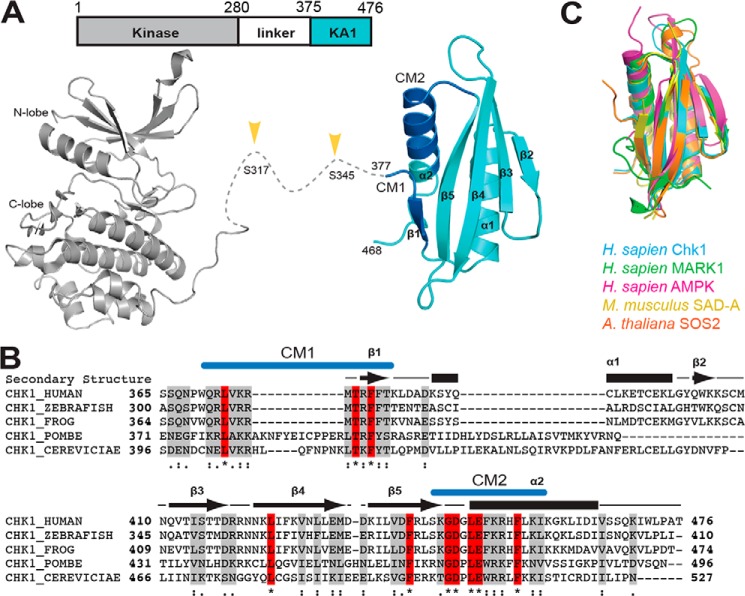
Figure 1.
Domain architecture and structure of Chk1. A, domain architecture (top) and crystal structures (bottom) of Chk1. Chk1 consists of a protein kinase domain (gray) (PDB code 1NVR) and a KA1 (cyan) domain (this work) connected by a ∼100-residue linker. Phosphorylation of the linker region (yellow arrows) by ATR kinase activates Chk1. The crystal structure of the KA1 domain reported here highlights the location of conserved motifs CM1 and CM2 (blue). B, multiple sequence alignment of KA1 domains from Chk1 orthologs with secondary structure (arrows for β-strands, bars for α-helices) of human Chk1 indicated. Identical (red, asterisk) and similar (gray, strongly similar: colon, or weakly similar, dot) positions are noted. Locations of CM1 and CM2 are indicated in blue. C, structural alignment of the KA1 domains of Homo sapiens Chk1 (this work, residues 377–468), MARK1 (PDB code 3OSE, 696–795, 18.7% sequence identity), AMPK (PDB code 4CFE, 404–473, 532–551, 18.1%), Mus musculus SAD-A (PDB code 4YOM, 533–636, 15.7%), and A. thaliana SOS2 (PDB code 2EHB, 337–430, 20.4%).