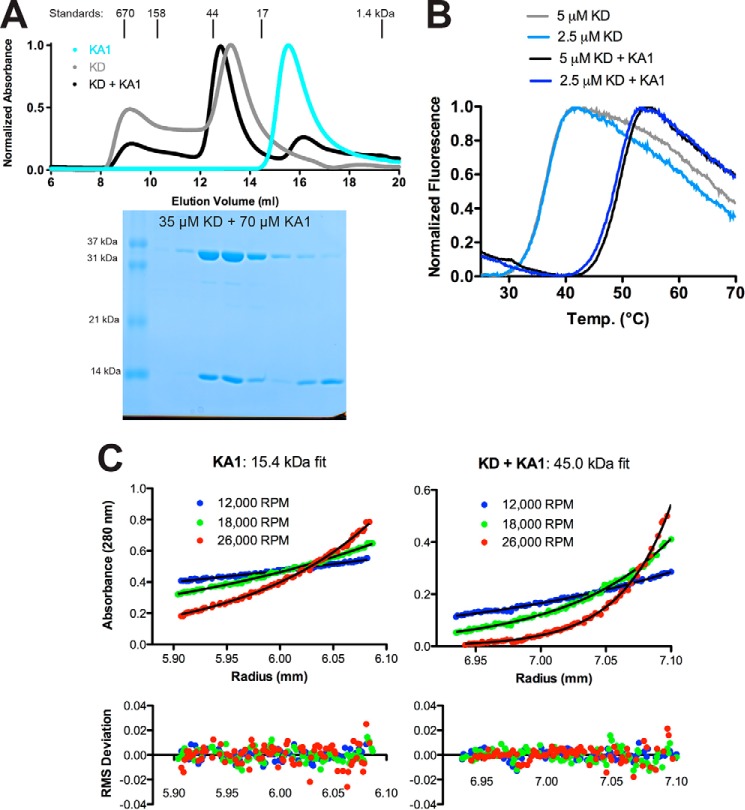
Figure 3.
Separately purified Chk1 kinase and KA1 domains interact in solution. A, size-exclusion chromatography profiles of recombinant Chk1 kinase domain (KD, 1–277) (gray), KA1 domain (366–476) (cyan), or a mixture of KD and KA1 domains (black) at a 1:2 molar ratio. Peaks were normalized to maximum absorbance at 280 nm. Peak positions and molecular weights of protein standards are indicated above the plot. An SDS-PAGE gel of fractions from the black trace is displayed below the chromatogram aligned with the curve. B, representative melting curves of KD alone (light blue and gray) or a mixture of KD and KA1 (blue and black) at 2.5 or 5 μm based on SYPRO Orange fluorescence. Mean ± S.D. melting temperature of six replicates were 36.6 ± 0.3 °C for kinase alone and 49.1 ± 0.4 °C for the mixture. Chk1 KA1 domain alone displayed a melting temperature of ∼50 °C (Fig. 5A). C, sedimentation equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation of a 24 μm Chk1 KA1 domain or an equimolar mixture of 4 μm KD and KA1 at the indicated speeds. The black lines represent global fits of the three indicated speeds at two concentrations (8 and 24 μm for KA1, 4 and 8 μm for the mixture). Data are representative of two independent protein preparations.