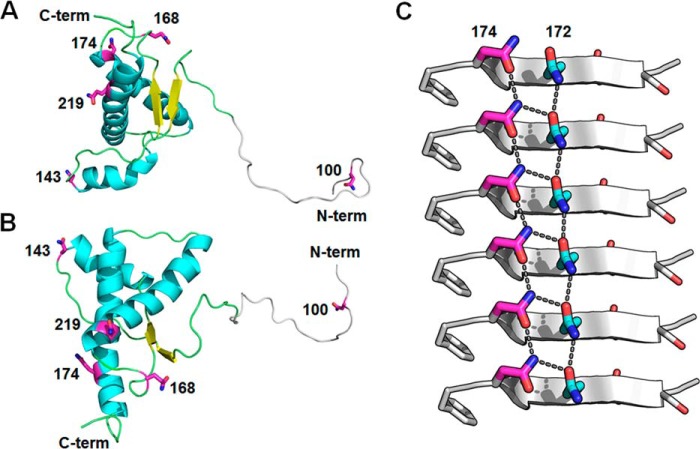
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism for prion conversion involving asparagine/glutamine residues in discrete segments of bank vole PrPC. A, a ribbon diagram of the NMR BvPrPC structure (Protein Data Bank code 2K56; Ref. 27) with critical Asn/Gln residues shown in magenta. The N-terminal domain of PrPC (residues 97–118, gray) is modeled using Rosetta software (63). Residues 23–96 are not shown. B, another view of the NMR BvPrPC structure rotated horizontally by 90°. C, zipper structure from PrPSc peptide (residues 170–175; Protein Data Bank code 3VFA; Ref. 36) fibril demonstrating that alignment of Asn/Gln residues along the length of the fibril axis promotes side chain hydrogen bonds in a motif known as an asparagine/glutamine-ladder. β-Strands are represented by gray arrows, Asm174 residues are shown in magenta, Gln172 residues are in cyan, and side chain hydrogen bonds in the asparagine/glutamine-ladder are indicated by black dotted lines.