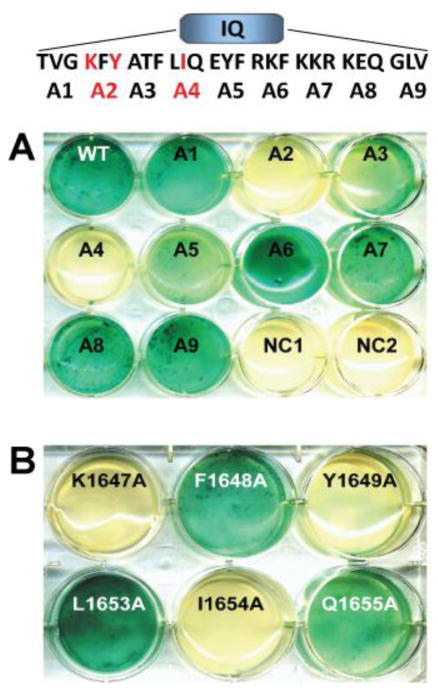
Figure 2. Defining AAs in the α11.2 IQ region required for α-actinin-1 binding.
A) Nine triple alanine mutations spanning AAs 1644-1670 within the IQ domain (see top sequence schematic showing placement of mutations) were engineered into pGBKT7 encoding α11.2 residues 1506-1871. Note that the inability of the two triple alanine mutants (red highlighted) A2 (KFY/AAA) and A4 (LIQ/AAA) to trigger conversion of X-α-Gal to the blue chromophore indicates loss of the α11.2 IQ bait polypeptide interaction with α-actinin-1 SR234EF prey polypeptide. Co-transformation of WT α11.2-pGBKT7 construct with blank pGADT7 plasmid (NC1) or blank pGBKT7 plasmid with α-actinin-1 pGADT7 construct (NC2) served as negative controls. B) The single alanine substitutions K1647A, Y1649A, and I1654A within the original WT α11.2 IQ A2 and A4 segments (highlighted in red in the sequence schematic in A) individually disrupted the interaction with the SR234EF prey (N=2 independent experiments).