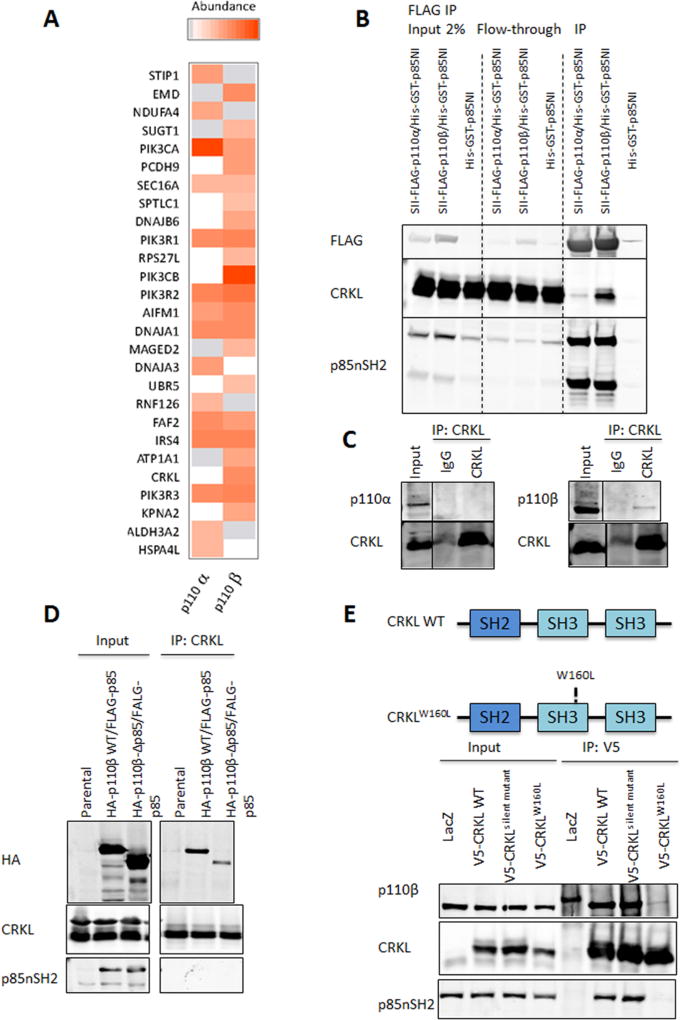
Figure 1. Identification of CRKL as a selective p110β interacting protein.
(A) p110α and p110β differentially associate with binding partners. Proteins reproducibly identified across two independent TAP experiments for p110α and p110β were quantified based on the average intensity of extracted ion chromatograms for the top three most abundant constituent peptides. The color intensity is proportional to the abundance of a protein relative to a given p110 isoform. Grey: proteins which were detected but not reliably quantified. White: proteins which were not detected.
(B) 293FT cells were transduced with BacMam viruses containing His-GST-p85NI, Strep (II)-FLAG-p110α/His-GST-p85NI, or Strep (II)-FLAG-p110β/His-GST-p85NI, followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG M2 agarose and immunoblot analysis with indicated antibodies.
(C) Endogenous CRKL was immunoprecipitated with anti-CRKL antibody from 293FT cell lysates. Rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) was used as a control. Cell lysates and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies.
(D) 293FT cells were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged bovine p85 and HA-tagged wild-type (p110β-WT) or mutant (p110β-Δp85) p110β. Cell lysates were prepared 2 d post-transfection followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-CRKL antibody and immunoblot analysis with indicated antibodies.
(E) CRKL requires its SH3N domain to efficiently interact with p110β. Top: Schematic illustration of wild-type and mutant CRKL. Bottom: Cell lysates from BT549 cells stably expressing LacZ control, V5-tagged wild-type or mutant human CRKL were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 antibody and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies.
See also Figure S1.