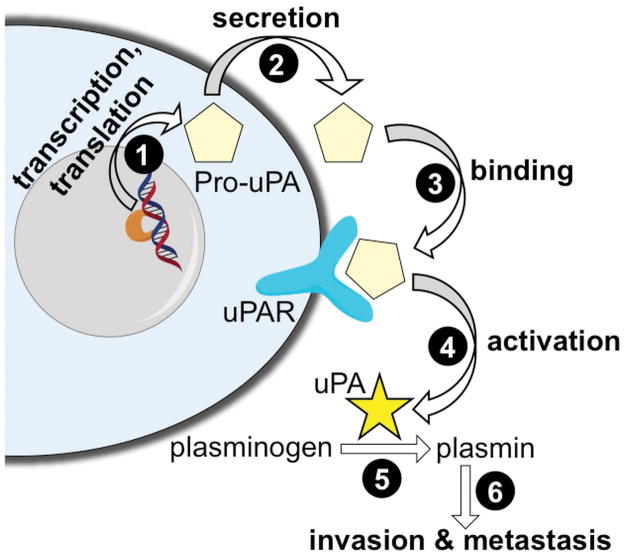
Figure 1.
A schematic of the expression, activation, and function of urokinase Plasminogen Activator (uPA). The inactive pro-uPA zymogen is transcribed and translated (step 1), and eventually secreted from the cell (step 2). After binding to the uPAR receptor (step 3), the pro-uPA is cleaved to become an active uPA enzyme (step 4). uPA can catalyze the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin (step 5), and plasmin then participates in processes that promote tumor invasion and metastases (step 6).