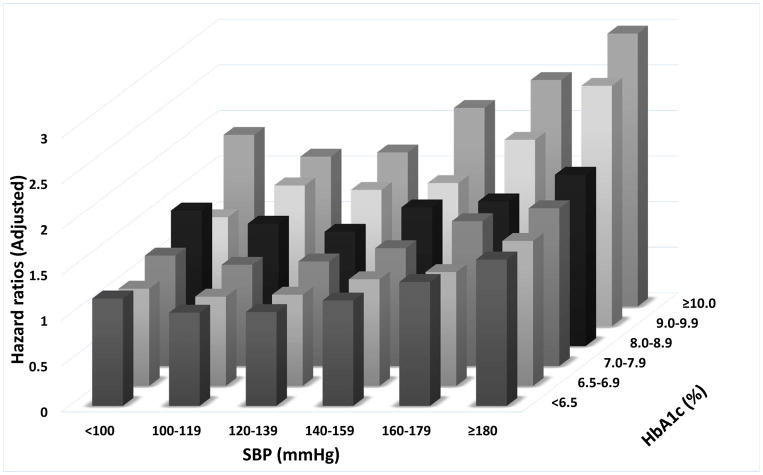
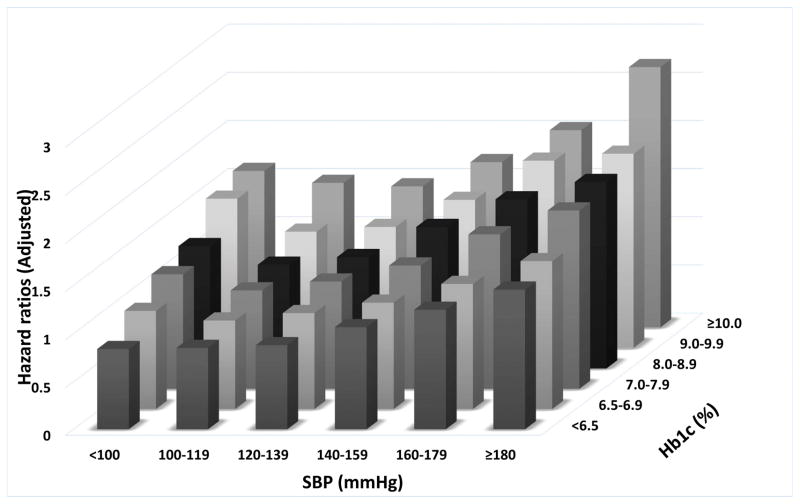
Figure 3.
Associations of blood pressure and A1c categories with the risk of cardiovascular disease (panel A), stroke (panel B) and chronic kidney disease (panel C).
The effects of the categories on the mortality risks were estimated from Cox proportional hazards models. Risk estimates were adjusted for the following factors at baseline: age, gender, race/ethnicity, baseline eGFR, various socio-economic parameters, service connection, adherence to medical interventions, comorbidities, body mass index and statin treatment. The adjusted hazard ratios are compared to the reference category of systolic blood pressure of 120–139mmHg and A1c of 6.5–7.0% taken as 1.0.