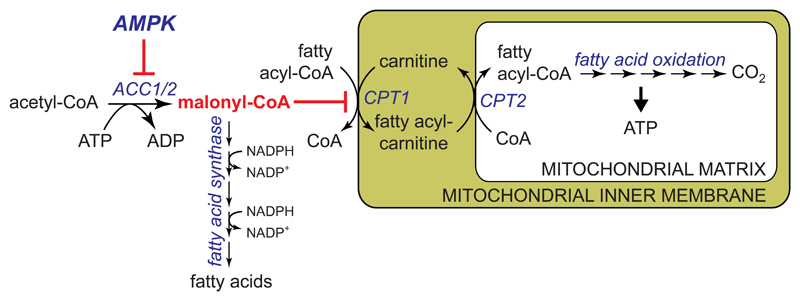
Figure 4. Acute activation of fatty acid oxidation and inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by AMPK.
AMPK phosphorylates both isoforms ACC1 and ACC2 at equivalent sites (Ser80 and Ser221 in human ACC1 and ACC2 respectively), causing their inactivation. This lowers malonyl-CoA, a key intermediate in fatty acid synthesis that is also an inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT1). CPT1 is involved in uptake of fatty acids into mitochondria, where they are oxidized to generate ATP. It was thought that ACC1 produced the pool of malonyl-CoA involved in fatty acid synthesis, and ACC2 a separate pool of malonyl-CoA that regulates CPT1 [117], but recent results suggest that these two pools cannot be completely distinct [77].