Figure 6.
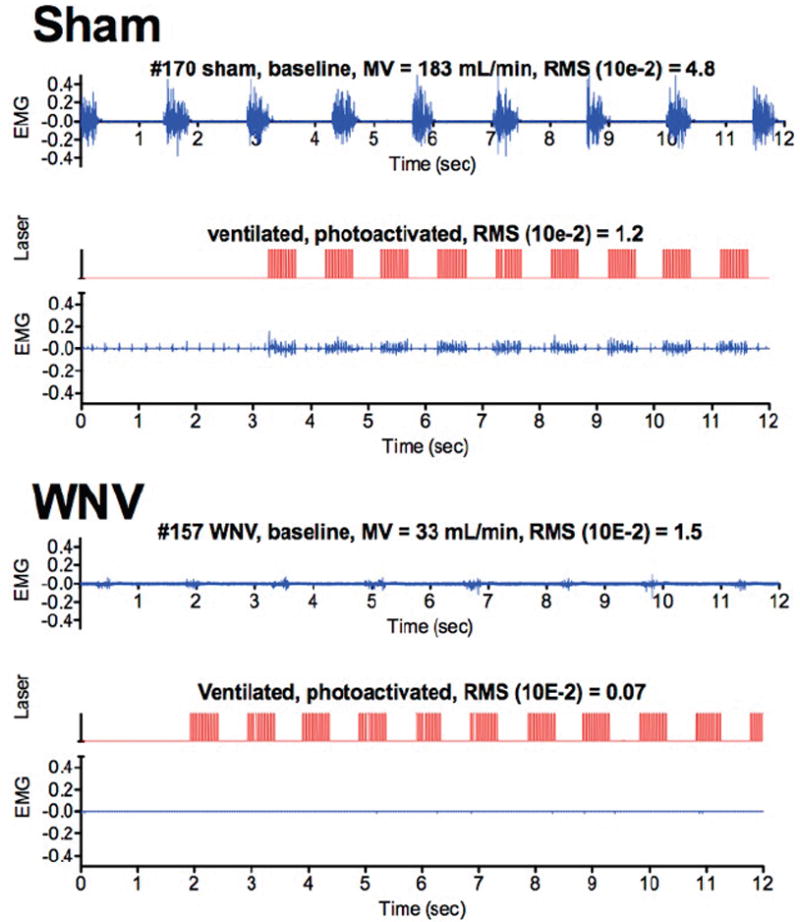
Effect of WNV infection on EMG of diaphragms of ChAT-mhChR2-YFP transgenic mice challenged with optogenetic photoactivation of C3-C4 cervical cord containing motor neurons innervating the diaphragm. Mice were infected with sham or WNV. Plethysmography was performed daily to detect the WNV-infected mice having MV values below 2SD of the normal MV values. The diaphragmatic EMGs of the mice with respiratory insufficiencies were then measured before (top EMG readings) and after intubation and vagotomy (not shown) to confirm the absence of EMG readings. An optical fiber was inserted between C3-C4 vertebrae (Morrey et al., 2008b). Diaphragmatic EMG was used to measure photoactivation of the phrenic neurons. The EMGs of the diaphragm (blue) were directly aligned with the photoactivation signals (red). (Adapted from Figure 1 in open-access publication (Wang et al., 2013b))
