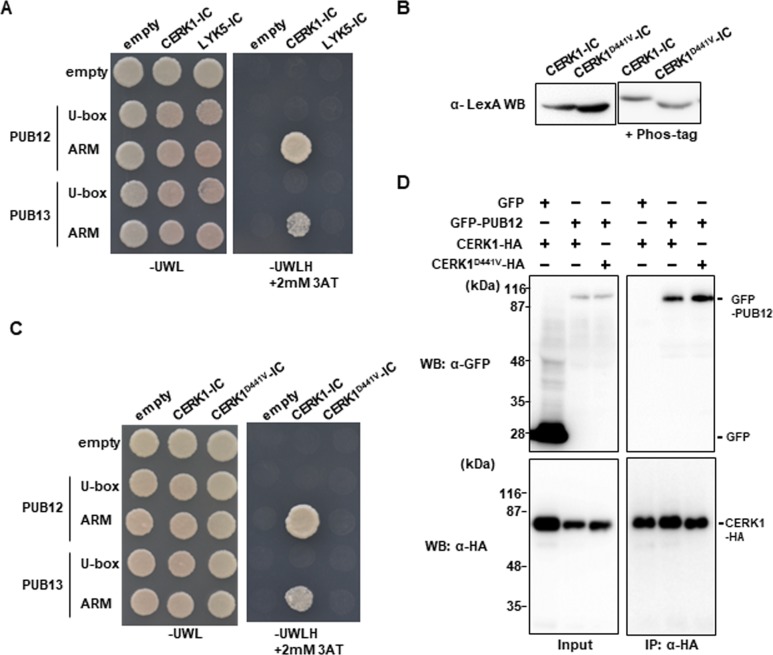
Fig 2. Interaction of PUB12 and PUB13 with CERK1 depends on its kinase activity.
(A) PUB12 and PUB13 interact with the intracellular domain (IC) of CERK1, but not LYK5 in the yeast two hybrid experiment. The growth of yeast colonies on plates (-ULWH) lacking uracil (U), leucine (L), tryptophan (W), and histidine (H) with 2 mM 3-aminotriazole (3-AT) indicates a positive interaction. (B) Immunoblot analysis of yeast extracts containing LexA fusion proteins. Total proteins were prepared from the yeast cells used for the two-hybrid assays in Fig 1B. Proteins were subjected to Phos-tag SDS-PAGE (right) or SDS-PAGE (left). Gels were analyzed by Western blotting with α-LexA. (C) PUB12 and PUB13 interact with CERK1-IC, but not the kinase-inactive mutant (CERK1D441V) in the yeast two hybrid experiment. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation assays show that PUB12-GFP forms a complex with the kinase-active and inactive forms of CERK1 in Nb leaves.