Figure 1.
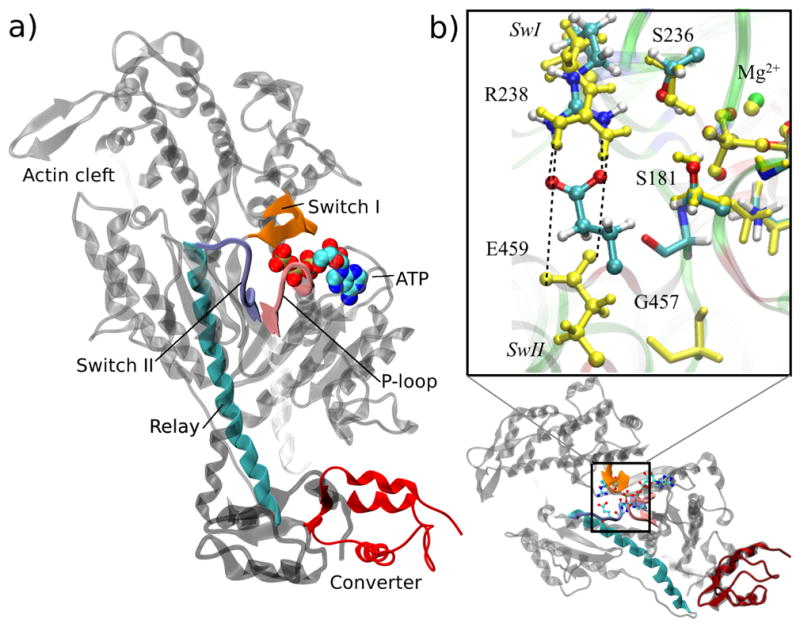
Structural transition between the post-rigor (PR) and pre-powerstroke (PPS) state of the myosin motor domain. (a) Overview of the myosin motor. The main structural elements involved in the mechanochemical coupling between ATP hydrolysis and mechanical motion are shown for the PPS conformation in color ribbon; these are Switch I, Switch II and P-loop in the nucleotide binding site, and the Relay helix connected to the Converter; the rest of myosin is drawn in light gray; ATP is drawn as color spheres. The displacements of the converter and the Relay in the transition to the PR structure are indicated in dark gray. (b) Expanded view of the nucleotide pocket centered on the QM region. Local transition in the active site largely involves the displacement of the SwII motif, leading to the break of the salt-bridge between Glu459 and Arg238 as well as displacement of Gly457 away from the γ-phosphate of ATP in PR (shown in yellow). Switch I and P-loop remain largely intact between the PR and PPS states.
