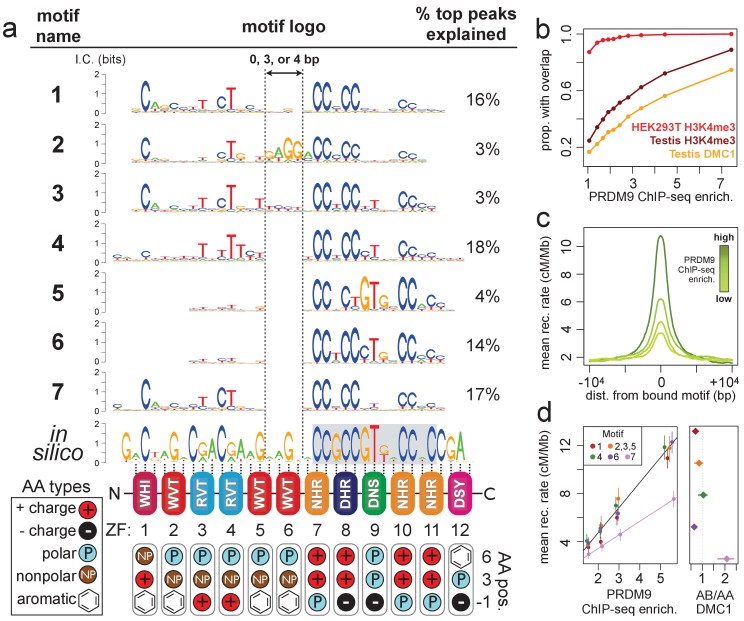
Figure 1. Comparison of seven distinct motifs bound by human PRDM9 (B allele).
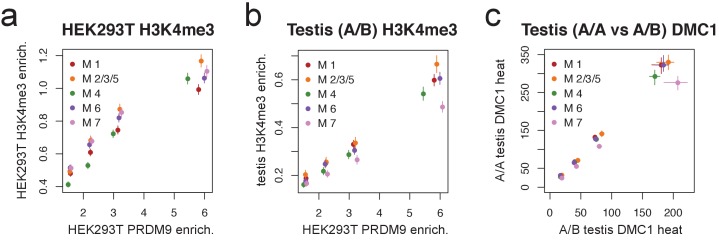
(a) Seven motif logos produced by our algorithm (applied to the top 5,000 PRDM9 binding peaks ranked by enrichment, after filtering out repeat-masked sequences) were aligned to each other and to an in silico binding prediction (Myers et al., 2010; Persikov et al., 2009; Persikov and Singh, 2014, maximizing alignment of the most information-rich bases. The position of the published hotspot 13-mer is indicated by the gray box overlapping the in silico motif (Myers et al., 2008). On the right is the percentage of the top 1,000 peaks (ranked by enrichment without further filtering) containing each motif type. Zinc-finger residues at 3 DNA-contacting positions (labeled −1, 3, 6) are illustrated below each ZF position, classified by polarity, charge, and presence of aromatic side chains. ZFs 5 and 6 lack positively charged amino acids and contain aromatic tryptophan residues, and they coincide with a variably spaced motif region (indicated by vertical dotted lines). Motif 4 is truncated here. (b) H3K4me3 ChIP-seq data from PRDM9-transfected HEK293T cells (this study) and H3K4me3/DMC1 data from testes (Pratto et al., 2014) were force-called to provide a p-value for enrichment of each sample in a 1 kb window centered on each PRDM9 peak (filtered to remove coverage outliers and those overlapping H3K4me3 peaks in untransfected cells). PRDM9 enrichment values are unitless (equal to the estimated signal divided by background, minus 1 and set to 0 if negative, at the base with the smallest p-value within each peak). Peaks were split into deciles according to their PRDM9 enrichment values, and the proportion of peaks with a force-called H3K4me3 or DMC1 p-value <0.05 is plotted within each decile. (c) Peaks were stratified into quartiles based on increasing PRDM9 enrichment (light green to dark green) after filtering out promoters. Mean recombination rates (from the HapMap LD-based recombination map, Frazer et al., 2007) at each base in the 20 kb region centered on each bound motif are plotted for each quartile, with smoothing (ksmooth, bandwidth 25). (d) Left plot: Peak enrichment quartiles (filtered to remove promoters as in c) were separated by motif type (Motifs 2, 3, and 5 were combined due to low abundance), and the mean HapMap CEU recombination rate overlapping peak centers was plotted against median PRDM9 enrichment in each quartile, with lines of best fit added for Motif 7 (pink) versus all other motifs. Right plot: Fold enrichment of each motif in AB-only DMC1 peaks versus AA-only DMC1 peaks (Pratto et al., 2014). Error bars indicate two standard errors of the mean (left plot) or 95% bootstrap confidence intervals (right plot).