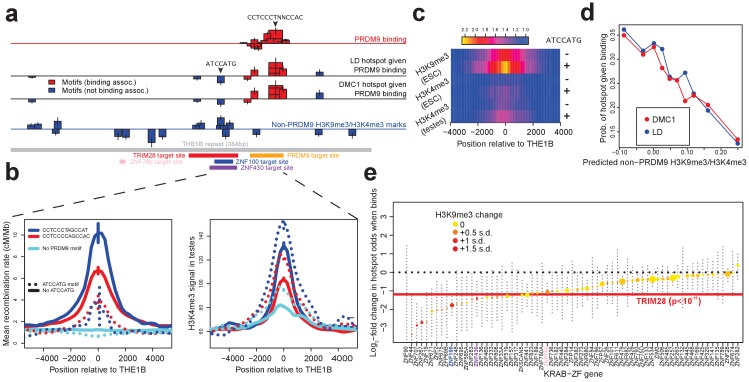
Figure 4. Influences on recombination in cis downstream of PRDM9 binding.
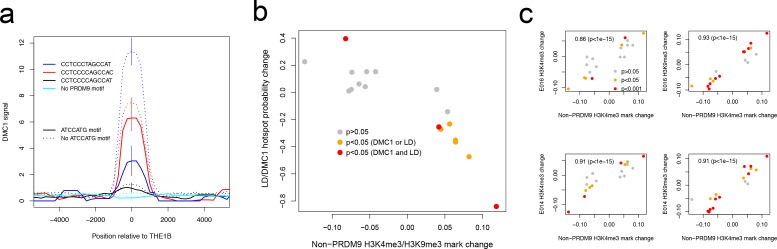
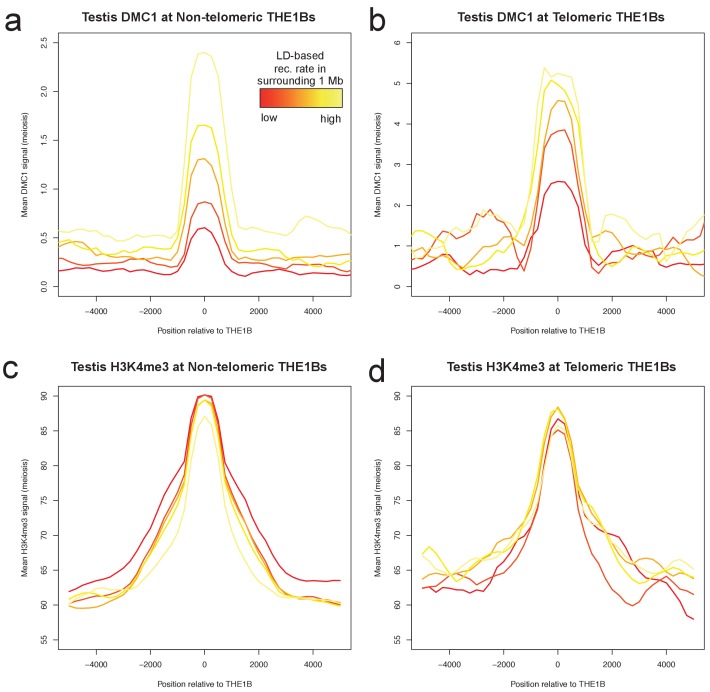
(a) Analysis of THE1B repeats shows the positions along the THE1B consensus (bottom, gray) of motifs influencing PRDM9 binding (top row), motifs influencing recombination hotspot occurrence at bound sites (middle two rows), and motifs influencing H3K4me3/H3K9me3 in testes and somatic cells (bottom row). Rectangle widths show motif size, and heights show log-odds-ratio or effect size (two standard errors delineated). Rectangles below the lines have negative effects. Motifs associated with PRDM9 binding are in red; others in blue. Binding motifs for labeled proteins are at the plot base. (b) Left plot shows LD-based recombination rates around the centers of THE1B repeats containing different approximate matches to the PRDM9 binding motif CCTCCC[CT]AGCCA[CT] (colors) and the motif ATCCATG (lines dotted if present). Right plot is the same but shows mean H3K4me3 in testes (from Pratto et al., 2014). ATCCATG presence reduces recombination and increases H3K4me3. (c) Impact of ATCCATG presence (+) or absence (-) on normalized enrichment values around the centers of THE1B repeats, of H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 in different cells (labeled pairs of color bars, normalized to equal 1 at edges). H3K9me3 shows the strongest signal increase. (d) Predicted non-PRDM9 H3K9me3/H3K4me3 versus probability DMC1-based or LD-based hotspots occur at PRDM9-bound sites. For the x-axis repeats were binned according to an additive DNA-based score, using the bottom row of part A and the combination of motifs they contained. (e) Estimated impact on whether a hotspot occurs of co-binding by individual KRAB-ZNF proteins (labels; Imbeault et al., 2017) near a PRDM9 binding peak (genome-wide, not only within THE1B repeats, after filtering out promoter regions). For each KRAB-ZNF protein, a GLM was used to estimate the impact of KRAB-ZNF binding (binary regressor) on hotspot probability. We show the estimated log-odds, with 95% CIs. Colors indicate H3K9me3 enrichment increase at co-bound sites. Horizontal line shows the results for TRIM28. Features below the horizontal dotted line have a negative estimated impact on downstream recombination.