Fig. 1.
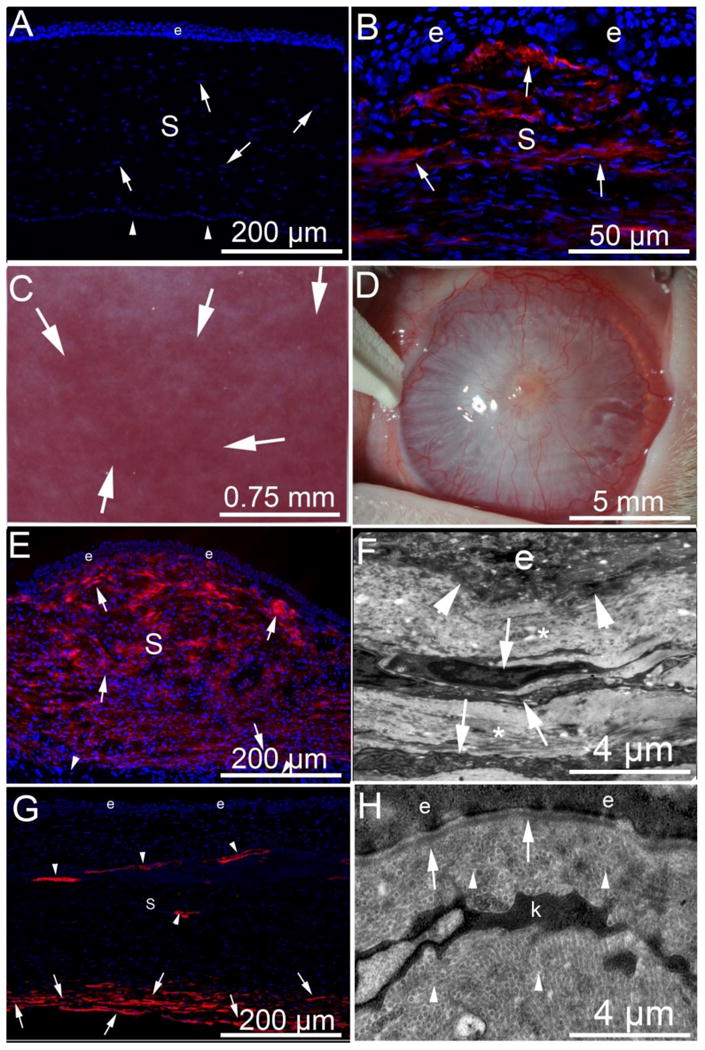
Fibrosis, myofibroblasts and the epithelial basement membrane after injury to the cornea. α-SMA (red) in immunohistochemistry (IHC). (A) α-SMA and DAPI IHC in a normal uninjured rabbit cornea with epithelium (e), the stroma (s) populated with stromal fibroblastic cells termed keratocytes (arrowheads, although a few of these nuclei could be Schwann cells associated with nerves) and corneal endothelium (arrows) that rests on Descemet's BM on the posterior surface of the cornea. Note there is no α-SMA in the unwounded normal cornea. Blue is DAPI staining of cell nuclei. Note, there are no α-SMA+ cells present. (B) α-SMA and DAPI IHC of a rabbit cornea at one month after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) surgery to correct high nearsightedness has alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) + myofibroblasts (arrows) in the anterior stroma beneath the epithelium. There are many DAPI+ nuclei in the stroma (S) and these are likely a heterogeneous population of cells including corneal fibroblasts, keratocytes, different bone marrow-derived cells such as fibrocytes and macrophages, and even Schwann cells associated with nerves. C. Slit lamp photo of a rabbit cornea at three months after PRK where clear areas (lacunae, arrows) have developed within the fibrosis. D. Slit lamp image of severe corneal fibrosis induced by pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis in a rabbit cornea at one month after infection and sterilization with antibiotics. E. α-SMA and DAPI IHC shows myofibroblasts (arrows) nearly full thickness of the stroma (s) at one-month after pseudomonas keratitis. Note that the posterior corneal stroma is normal with α-SMA-negative keratocytes (arrowheads). e is epithelium. F. TEM of cornea at one-month after pseudomonas keratitis. Normal EBM lamina lucida and lamina densa cannot be recognized at the epithelio-stromal junction (arrowheads). e is epithelium. The anterior stroma has stacked myofibroblasts (arrows) with large amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum that correspond to α-SMA+ cells in Fig. 1E and the surrounding extracellular matrix (*) is disorganized without detectible uniform fibrils. G. α-SMA and DAPI IHC at three months after pseudomonas keratitis that extended more posterior than in the cornea in Fig. 1E, and consequently also damaged the endothelium and Descemet's BM. Most anterior stromal α-SMA+ myofibroblasts have disappeared after regeneration of the epithelial BM noted with TEM (Fig. 1H), but α-SMA+ myofibroblasts persist in the posterior stroma (arrows) where Descemet's BM and the endothelium remain damaged or absent. Neovascular blood vessels persist in the stroma and have associated α-SMA+ pericytes (arrowheads). H. TEM of epithelial-stromal junction at three-months after pseudomonas keratitis. Normal EBM lamina lucida and lamina densa are present (arrows) and likely a keratocyte (k), but possibly a nerve-associated Schwann cell, is present, but myofibroblasts with large amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum have disappeared [15]. Also note, normal regular collagen fibrils (arrowheads) are now present throughout the anterior stromal shown.
