Figure 5. EVs containing human α-synuclein are internalized by primary cerebral cortical neurons.
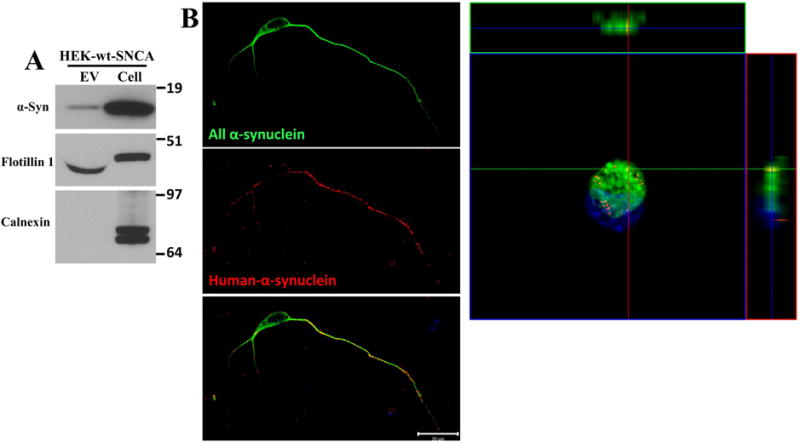
(A) EVs were isolated from the culture medium of HEK cells overexpressing wild type α-synuclein, and proteins in the EVs and the cells that released the EVs were separated in a NuPAGE Bis-Tris gel and immunoblotted using antibodies against human α-synuclein, flotillin-1 (EV marker protein) and calnexin (a protein not known to be in EVs). (B) Cerebral cortical neurons were treated with HEK-wt-SNCA EVs at a concentration of 20 μg/ml for 2 hours. Neurons were then fixed and immunostained with an α-synuclein antibody that recognizes both human and rat α-synuclein (C20 antibody, green) and an antibody specific for human α-synuclein (Syn211 antibody, red). Confocal images reveal EV-derived human α-synuclein immunoreactivity within the axon, and to a lesser extent in the cell body and dendrites of a recipient neuron. The Z-stack image shows the distribution of EV-derived human, and endogenous rat α-synuclein, in the cell body of the same neuron shown at the left. These images are representative of 20 neurons examined in 3 independent experiments. Scale bar, 20 μm.
