Figure 7. Evidence that α-synuclein is present within and on the surface of EVs, and that EV surface-associated α-synuclein enhances EV internalization by recipient neurons.
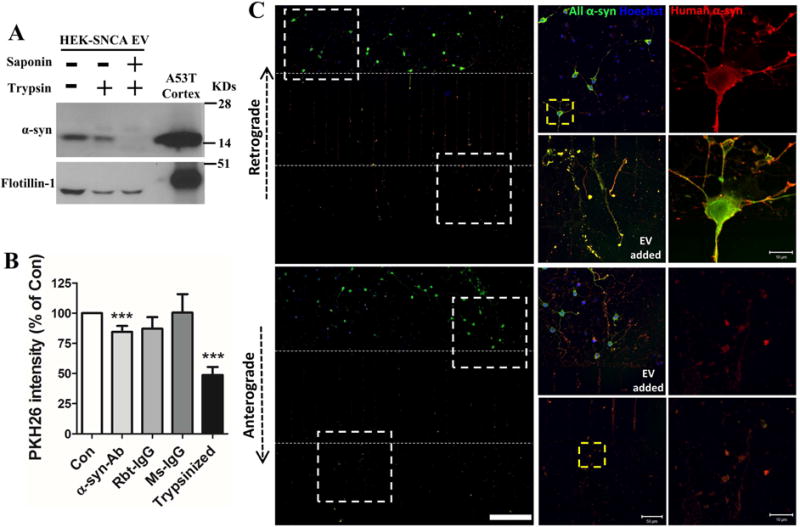
(A) EVs isolated from HEK-wt-SNCA cells were subjected to trypsin digestion without or with EV membrane permeabilization (see Methods). Proteins in the EVs and mouse cortical tissue were separated in a NuPAGE Bis-Tris gel and immunoblotted with α-synuclein and flotillin-1 antibodies. (B) Control and trypsin digested EVs from HEK-wt-SNCA cells were labeled with fluorescent PKH26 dye. EVs were preincubated with or without human α-synuclein antibody, rabbit IgG, or mouse IgG for 30 minutes before being added to the medium of cortical neurons cultured in 96 well plates. Neurons were incubated with the different EV preparations for 2 hours and the fluorescence intensity of PKH26 inside neurons was quantified in a plate reader. Values are the mean and SEM of determinations made in 3–5 independent experiments. ***p<0.001 compared to the control value. (C) Rat primary cortical neurons were grown in microfluidic chambers for 10 days. EVs released from HEK-wt-SNCA cells were then added to the medium of either the axonal compartment (upper panels) or the somatodendritic compartment (lower panels), and 4 hours later neurons were fixed and immunostained with anti-pan α-synuclein (green) and anti-human α-synuclein (red) antibodies. Confocal images show EV-derived human human α-synuclein immunoreactivity in axons, and the cell body and dendrites. The region of the image demarcated by the dashed white squares in left low magnification images are enlarged in the middle panels. The region of the image demarcated by the dashed yellow square in the middle panels are enlarged in right panels. Scale bar = 200 μm in panels at left, 50 μm in panels in middle, and 10 μm in the panels at the right.
