Figure. 2.
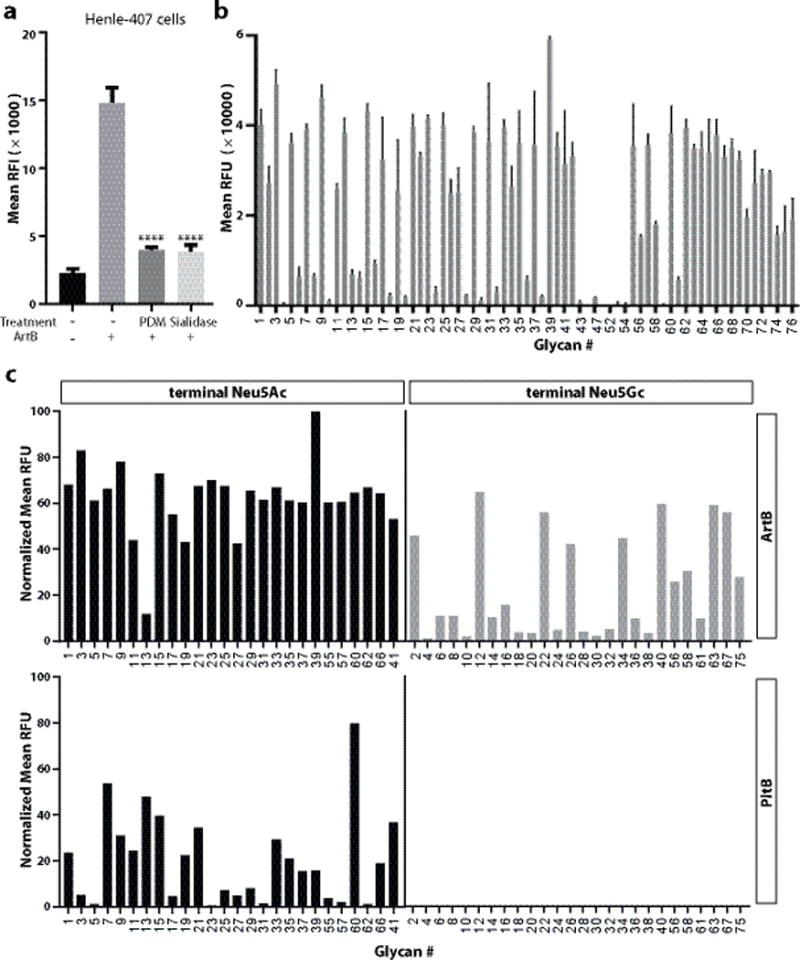
ArtB binds Neu5Ac- and Neu5Gc-terminated glycans. a, Removal of surface glycans reduces ArtB binding to cultured cells. Henle-407 cells were treated with a mixture of glycosidases (PDM, protein deglycosylation mix) or a sialidase (α2–3/6/8-neuraminidase) and the ability of treated and control cells to bind fluorescently labeled ArtB (2.5 μM) was evaluated by flow cytometry. The y-axis values represent the relative fluorescence intensity (RFI). Bars represent mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent measurements. Two-tailed Student’s t tests were performed to determine the statistical significance for two group comparisons. ****: P<0.0001, compare to the relative fluorescence intensity of ArtB-binding to the untreated cells. b, ArtB-binding to a customized glycan microarray. The y-axis values represent average and standard deviation of the relative fluorescence units (RFU) from four independent experiments, and the x-axis indicates the glycan numbers (see also Table S1). c, Comparison of ArtB-binding to paired Neu5Ac- and Neu5Gc- terminated glycans. The y-axis values represent the normalized average relative fluorescence units (RFU) from four independent experiments and the x-axis depicts the glycan numbers (see also Table S2).
