Figure 4.
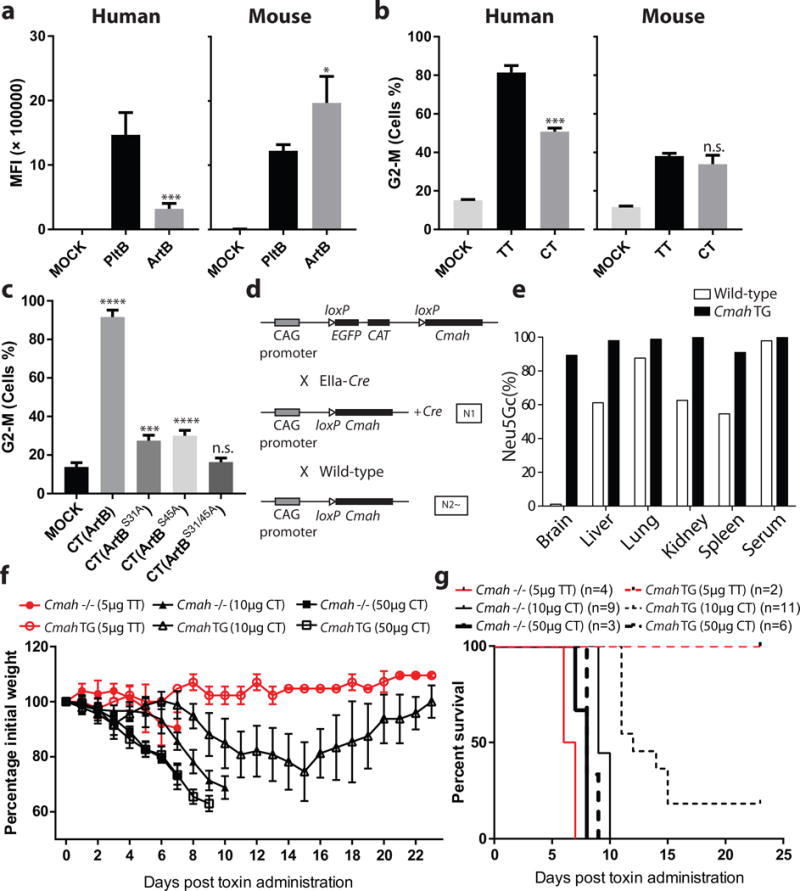
The ArtB/PltA/CdtB chimeric toxin exhibits reduced lethality in mice relative to typhoid toxin. a, ArtB and PltB (2. 5 μM each) binding to human (Henle-407) or mouse (embryo fibroblasts) cells. The binding of fluorescently-labeled PltB and ArtB was evaluated by flow cytometry. The y-axis values represent the mean fluorescence index (MFI) and are the mean ± SD of at least three independent measurements. *: p < 0.05; ***: p < 0.0005. b, Relative toxicity to human (Henle-407) or mouse (embryo fibroblasts) cells of purified typhoid toxin (TT) (3 pM) and ArtB/PltA/CdtB chimeric toxin (CT) (3 pM). The percentage of cells in G2/M, a measured of CdtB toxic activity, after application of the indicated toxins was determined by flow cytometry. Data are the mean ± SD of at least three independent determinations. ***: p < 0.0005, n.s. (no significance): p>0.05 compared to untreated cells. c, Relative contribution of the different ArtB glycan-biding sites to toxicity. Different ArtB/PltA/CdtB chimeric toxin (CT) preparations containing the indicated ArtB mutants were tested for their ability to intoxicate cultured cells. Equal amounts (250 pM) of chimeric toxin preparations were applied to the cultured cells and the percentage of cells in G2/M was determined by flow cytometry. Data are the mean ± SD of at least three independent determinations. ****: p < 0.0001, ***: p < 0.0005, n.s. (no significance): p>0.05 compared to untreated cells. In a-c two-tailed Student’s t tests were performed to determine the statistical significance for two group comparisons. d, Scheme of the strategy used to generate a Cmah TG mouse. Targeted Cre-inducible Cmah TG mice (transgene insertion in H11 locus, top) were crossed with EIIa-Cre mice that induce Cre expression at the preimplantation embryo stage and the resulting N1 generation mouse with the Cmah transgene and Cre was further mated with wild-type mice. Among the resulting N2 generation, the mice that had Cmah transgene but lacked Cre were selected as systemic Cmah TG mice and maintained by crossing with wild-type mice. e, Tissue homogenates obtained from 11-week-old male mice were hydrolyzed in 2M acetic acid to release sialic acids after treatment with 0.1M sodium hydroxide to remove O-acetylation of sialic acids. The percentage of Neu5Gc in total sialic acids was determined by HPLC using DMB-derivatization method. Each bar represents the average of samples from two mice per genotype. Cmah TG mice showed remarkably high Neu5Gc expression in all tissues tested. f and g, Mouse toxicity of the ArtB/PltA/CdtB chimeric toxin relative to typhoid toxin. Cmah −/− or Cmah transgenic (TG) mice were administered intraorbitally either typhoid toxin (TT) (5μg) or ArtB/PltA/CdtB chimeric toxin (CT) (10 or 50 μg) and their body weight (f) and survival (g) at the indicated times were recorded. Values in (f) are the mean and standard deviations. The difference in weight loss between groups (f) was analyzed by the Mann-Whitney test (TT vs CT in Cmah TG: p <0.0001, TT vs CT in Cmah −/−: p<0.05). The difference in survival (g) was analyzed by the Mantel Cox test. (TT vs CT in Cmah TG: p <0.05; TT (5 μg) vs CT (10 μg) in Cmah −/−: p <0.001.
