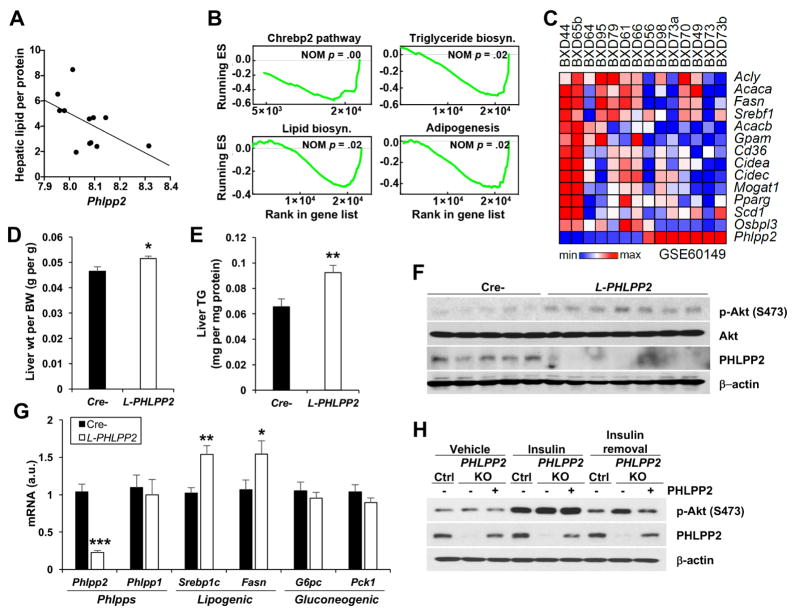
Figure 1. Loss of Phlpp2 causes fatty liver.
(A) Hepatic Phlpp2 expression negatively correlates with hepatic lipid across different BXD populations (Spearman rho = −0.60, p = .04). (B) Normalized enrichment score (ES) of GSEA indicating gene sets that show the most significant negative correlation with hepatic Phlpp2 expression. (C) Heat map showing co-regulation of Phlpp2 and lipogenic genes in BXD strains. (D) Liver weight and (E) triglycerides, (F) western blots of liver lysates and (G) hepatic gene expression in chow-fed liver-specific PHLPP2 knockout (L-PHLPP2) and Cre- control mice (n=9–10/group). (H) Western blots from control, PHLPP2 KO, or PHLPP2-reconstituted PHLPP2 KO cells “pulsed” with 10 nM insulin for 30 min, with or without a 2 h “chase” in insulin-free medium. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 as compared to the indicated control by two-way ANOVA. All data are shown as the means ± s.e.m.