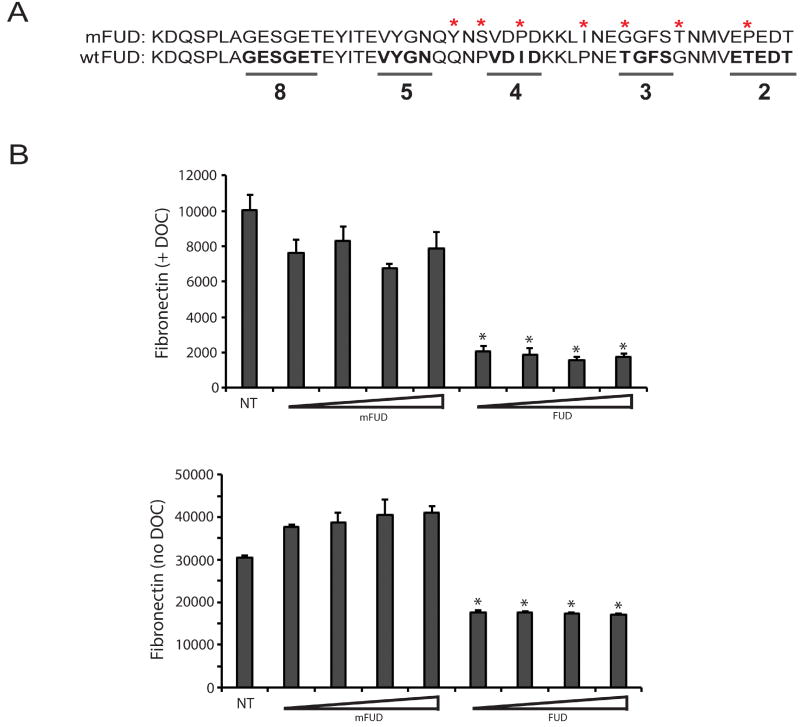
Figure 3. Inhibition of fibronectin fibrillogenesis by FUD is specific.
A) FUD was mutated using site-directed mutagenesis to alter key amino acids found within the C-terminal portion of the peptide in order to abrogate the activity the peptide. The bottom sequence is wild type FUD while the mutant FUD (mFUD) sequence is on top. The mutated amino acids are marked with asterisks. The underlined wild type sequences in bold are critical for FUD binding to fibronectin. The numbers 2, 3, 4, 5 & 8 indicate the fibronectin type I domains that the underlined sequences bind to (N-terminal to C-terminal) (Ma et al., 2015). B) HTM cells were plated at 25,000 cells/well into 96 wells plates and allowed to attach for 3 h. Cells were then left either untreated (NT) or treated with 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 or 4.0 µM mFUD or FUD for 24 h. Cell layers were then extracted with 1% DOC (top graph) or left un-extracted (bottom graph) prior to processing for OCW analysis. For both graphs, all FUD-treated groups are significantly less than untreated cells, p < 0.0001.