Figure 1.
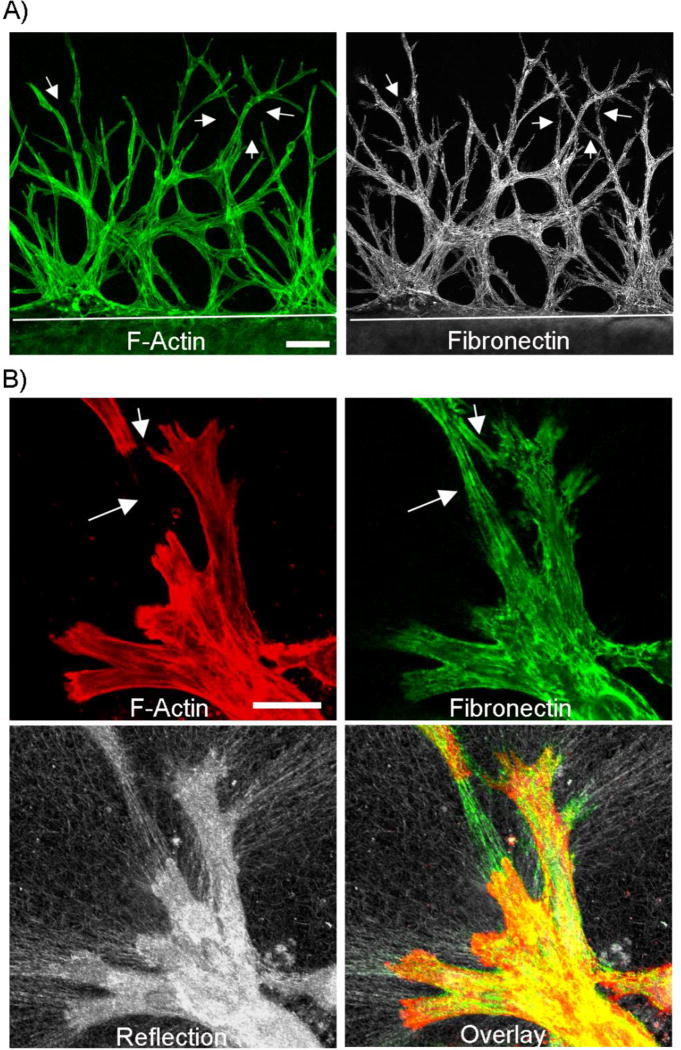
Fibroblasts migrating through fibrin create fibronectin tracks. Nested matrix constructs were cultured for 48h in PDGF-containing media to stimulate cell migration. A) Corneal fibroblasts form an interconnected network as they migrate into the outer fibrin matrix (top part of image, white line delineates edge of inner matrix). This network contained significant fibronectin. As shown by arrows, fibronectin “tracks” were sometimes present in between cells. Scale bar is 100 µm. B) Higher magnification images from a sample that was not permeabilized prior to fibronectin labeling. Extracellular fibronectin tracks were observed around cells. Fibronectin tracks were also found in spaces between cells in some areas (arrows). As shown by reflection microscopy, localized ECM compaction was produced by migrating fibroblasts. Scale bar is 100 µm.