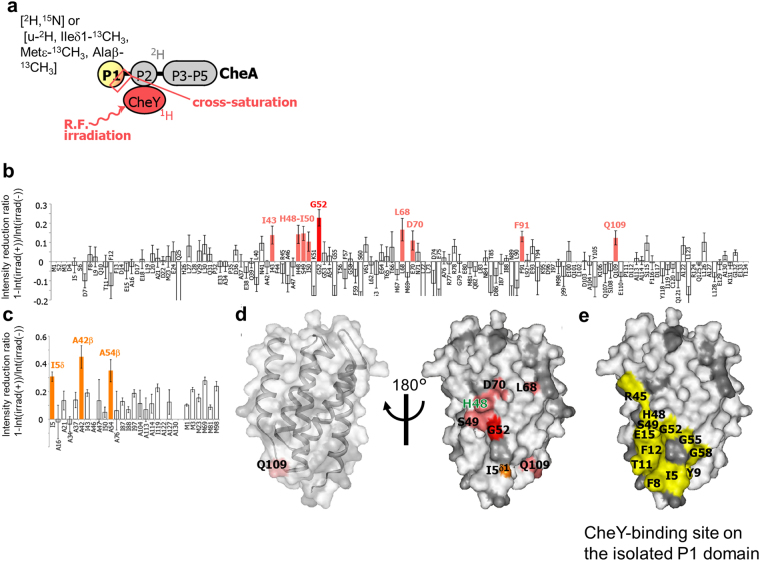
Figure 7.
CheY-binding interface on the P1 domain of CheA revealed by cross-saturation experiments using segmentally labeled CheA. (a) Schematic diagrams of the experiments. (b) Plots of the reduction ratios of the signal intensities originating from the amide groups. Red and light orange plots represent the residues with signal intensity reduction ratios > 0.2 and within the 0.1–0.2 range, respectively, and are labeled. (c) Plots of the reduction ratios of the signal intensities originating from the methyl groups in the cross-saturation experiments using [u-2H, Ileδ1-13CH3, Metε-13CH3, Alaβ-13CH3] CheA and non-labeled CheY. Orange plots represent the residues with signal intensity reduction ratios > 0.3. In (b,c), the residues with reduction ratios < 0.1 and < 0.3 are white, respectively, and the error bars represent the root sum square of the reciprocal of the signal-to-noise ratio of the resonances with and without irradiation. (d) Mapping of the residues on the P1 domain of CheA affected by the irradiation in the cross-saturation experiments (PDB ID: 1I5N). The residues with amide proton signal intensity reduction ratios > 0.2 and within the 0.1–0.2 range are colored red and light orange, respectively, and the residues with methyl proton signal intensity reduction ratios > 0.3 are colored orange. Proline residues and residues with intensity reductions that were not determined, because of low signal intensity or spectral overlap, are gray. In the left view, the surface of the P1 domain is transparent, and the ribbon diagram is simultaneously displayed. F91, A42β, and A54β, which are close to H48, are hidden in these views. (e) CheY-binding interface in the model of the E. coli isolated P1 domain-CheY (PDB ID: 2LP4), mapped on the structure of the P1 domain (PDB ID: 1I5N). The labeling and coloring schemes are the same as in Fig. 6f. The molecular diagrams were generated with Web Lab Viewer Pro (Molecular Simulations, Inc.).