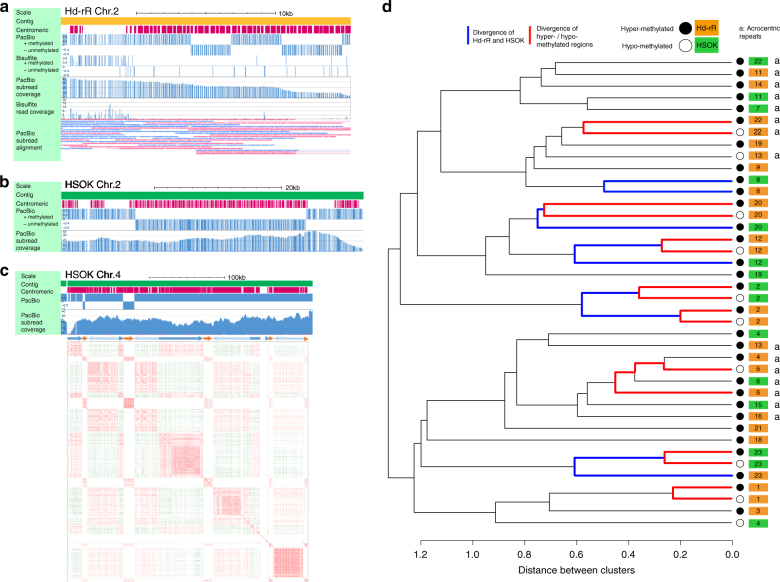
Fig. 3.
CpG methylation in centromeric repeats. a The tracks shown are, from the top, contigs layout as yellow bands, centromeric repeats as red bands, regional methylation prediction from PacBio reads (+, methylated; −, unmethylated), CpG-wise methylation from bisulfite reads, coverage of PacBio reads, coverage of bisulfite reads, and PacBio subreads alignments (red, forward; blue, reverse). Methylation calls by PacBio and bisulfite sequencing are inconsistent around the two unmethylated regions because most of bisulfite read coverages are very small (only 1) and are unreliable due to the repetitiveness of the centromeres. By contrast, PacBio reads achieved stable coverage over the repeat region. b A part of HSOK chromosome 2 with an unmethylated region that is syntenic to the region in Fig. 3a according to genetic markers (Fig. 1b). No bisulfite-treat short reads are available for the HSOK strain. c A ~305 Kbp centromeric repeat region in HSOK chromosome 4. The lower portion shows a dot plot of the region. Forward and reverse matches are colored red and green, respectively. Each dot represents 40-mer sequence match. Blue and orange arrows displayed above the dot plot show two patterns of centromeric repeats that do not match. A light blue arrow is inverse orientation of a blue arrow. d We clustered all hyper- and hypomethylated centromeric regions in Hd-rR and HSOK with at least 40 CpGs that we could reliably estimate from SMRT sequencing information (Methods, Supplementary Fig. 5). The respective orange and green boxes represent the Hd-rR and HSOK strains. The black and white circles illustrate hyper- and hypomethylated regions. Numbers indicate chromosome numbers. Black, blue, and red lines in the dendrogram respectively illustrate the timing of chromosome segregation, divergence of two strains (Hd-rR and HSOK), and divergence of hyper/hypomethylated regions in an identical chromosome of the same strain. Seven pairs of hypomethylated and hypermethylated regions (from top to bottom: Hd-rR chr. 22, 20, 12 HSOK chr. 2, Hd-rR chr. 2, HSOK chr. 23, Hd-rR chr. 1) are most similar to each other except for three exceptional cases (Hd-rR chr. 13, Hd-rR chr. 6, HSOK chr. 4). The rightmost column labels acrocentric repeats with “a”