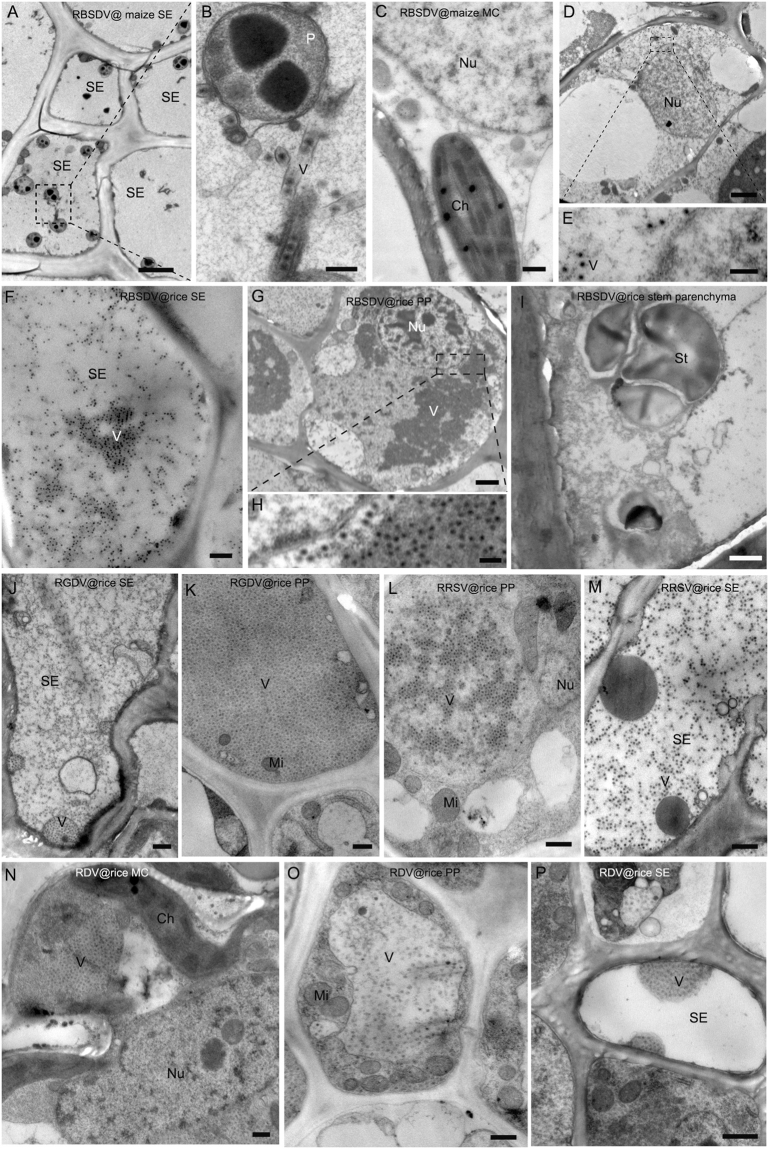
Figure 1.
Cellular distribution of different reoviruses in plant hosts. (A–E) RBSDV in maize leaf. (A,B) RBSDV virus-like particles (VLP) in SE in infected phloem. (Bar in G = 2 μm; Bar in H = 200 nm). (C) No virion was detected in MCs from infected leaves. (Bar = 500 nm). (D,E) Virion distribution in PP in the infected phloem. (Bar in D = 2 μm; Bar in E = 200 nm). (F–I) RBSDV in rice stem. (F) Virion distribution in SE in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm). (G,H) Virion distribution in PP in the infected phloem. (Bar in G = 2 μm; Bar in H = 200 nm). (I) No virion was detected in the stem parenchyma of infected plant. (Bar = 1 μm). (J,K) RGDV in rice leaf. (J) Virion distribution in SE in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm). (K) Virion distribution in PP in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm). (L,M) RRSV in rice leaf. (L) Virion distribution in PP in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm). (M) Virion distribution in SE in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm). (N–P) RDV in rice leaf. (N) Virion distribution in leaf MC infected with RDV. (Bar = 500 nm). (O) Virion distribution in PP in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm). (P) Virion distribution in SE in the infected phloem. (Bar = 500 nm).