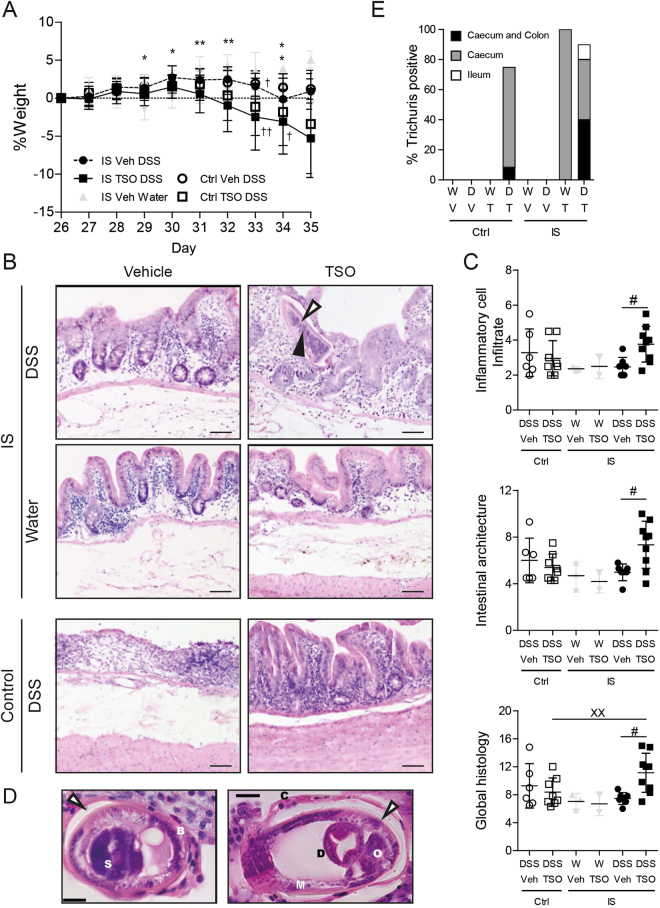
Figure 7.
Immunosuppression abrogates the protective effects of TSO and exacerbates the DSS induced damage and inflammation of the caecal mucosa. (A) Body weight change relative to the baseline at DSS colitis induction (day 26). (B) Representative HE stained specimens of caecal mucosa (day 35). IS: immunosuppressed rabbits, control: immunocompetent rabbits. Bars = 100 µm. 3 specimens per rabbit were assessed. Filled arrowhead: T. suis schistosome. (C) Inflammatory cell infiltrate score based on the lymphocyte infiltrate into the lamina propria and epithelium (2–8). Intestinal architecture score based on independent scoring of villous stunting, epithelium damage and crypt distortion (3–12). Inflammatory cell infiltrate and intestinal architecture score were summarized to a combined histology score (5–20). (D) HE stained section of the caecal mucosa of IS TSO-DSS rabbits showing the presence of adult T. suis. Left panel: longitudinal section of the posterior part; Right panel: cross section of the posterior end of the parasite. S: stychosome nucleus; Bb: bacillary band; C: cuticle; O: reproductive organs; D: digestive tract; M: muscle layer. Bars = 20 µm. Empty arrowhead: syncytial tunnel derived from the host’s caecal epithelium. (E) Percentage of animals tested positive for Trichuris by PCR in different regions of the gastrointestinal tract (caecum, colon and ileum). W: water, D: DSS, V: Vehicle, T: TSO, Ctrl: Control, IS: immunosuppressed. Dots represent single animals, bars represent mean ± SEM, data were pooled from three independent experiments, n = 2–4 animals per group. *P < 0.05, **P < .01, two-sided p-Value, Mann-Whitney test between IS Veh DSS (n = 8‡) and IS TSO DSS (n = 9‡). ‡Number of animals at the start of the experiment. 3 IS TSO DSS and 1 IS Veh DSS animals reached the euthanasia criteria and were sacrificed at the indicated time point (†).