Fig. 3.
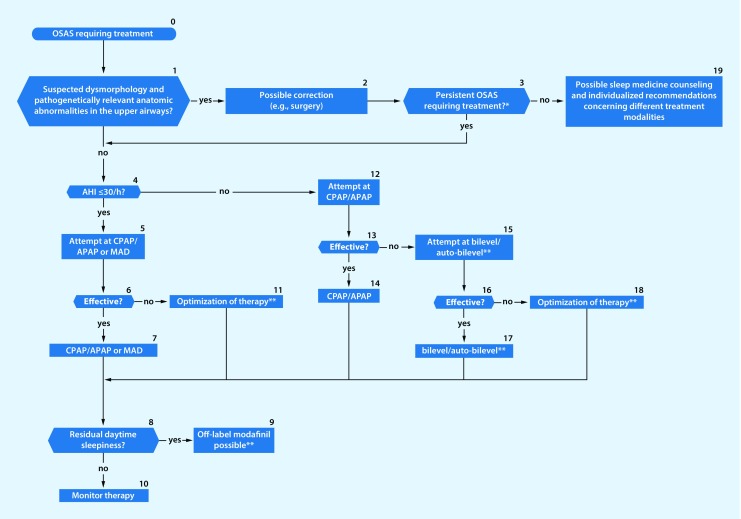
Algorithm for treatment of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. *Patient training, behavioral recommendations, sleep medicine counselling; in overweight patients, weight reduction should be attempted in parallel. **In patients with an apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) ≤30/h and lifelong obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), positional therapy can be considered if no other therapy is possible or tolerated. Mandibular advancement devices (MAD) can also be considered in patients with severe sleep apnea who do not tolerate or refuse continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), or in whom CPAP therapy cannot be used despite utilisation of all support measures. Where positive airway pressure therapies or MAD fail, in the absence of anatomic abnormalities and the presence of an AHI of 15–50/h, neurostimulation of the hypoglossal nerve (NSHG) can be used up to class I obesity, provided there is no concentric obstruction of the airways. (OSAS obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, APAP automatic CPAP)
